Effects of immune cells on ischemic stroke and the mediating roles of metabolites
- PMID: 38863512
- PMCID: PMC11165215
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1405108
Effects of immune cells on ischemic stroke and the mediating roles of metabolites
Abstract
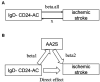
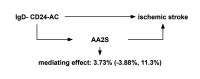
Objective: Previous studies have not shown an association between IgD-CD24-B-cell absolute count (IgD-CD24-AC) and ischemic stroke (IS). Our study aimed to assess the causal effect of IgD-CD24-AC on IS and to explore the role of ascorbic acid 2-sulfate (AA2S) as a potential mediator.
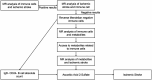
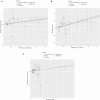
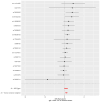
Methods: Our study was based on the largest available genome-wide association study (GWAS). Inverse variance weighting (IVW), MR-Egger, weighted median (WMN), simple mode, and weighted mode methods were used to assess causal effects, with IVW as the primary outcome. Subsequently, we further performed a two-step MR analysis to evaluate whether AA2S mediated this causal effect. In addition, several sensitivity analyses were conducted to evaluate heterogeneity, including Cochran's Q test, the MR-Egger intercept test, the MR-PRESSO global test, and the leave-one-out analysis.
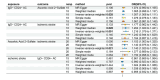
Results: Using the IVW approach, the risk ratio of IgD-CD24-AC to IS was estimated to be 1.216 (95% CI = 1.079-1.371, p = 0.001). This result was supported by the WMN method (OR = 1.204, 95% CI = 1.020-1.421, p = 0.028) and the MR-Egger method (OR = 1.177, 95% CI = 0.962-1.442, p = 0.133). We also observed the same trend with the simple model and weighted model. Furthermore, the proportion of genetically predicted IgD-CD24-AC mediated through AA2S levels was 3.73%.
Conclusion: Our study revealed a causal relationship between IgD-CD24-AC and IS, a small part of which was mediated by AA2S. These findings offer critical insights for developing immune-targeted therapies in the future and lay a strong foundation for advancements in precision medicine.
Keywords: AA2S; IgD-CD24-AC; Mendelian randomization; immunology; ischemic stroke; metabolite.
Copyright © 2024 Hu, Zhou, Zhao, Mao and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Causal associations of BAFF-R on IgD+ CD24- B cell immune cell trait with hepatocellular carcinoma and the mediating role of phenylacetylglutamate levels: a Mendelian randomization study.J Cancer. 2024 Jun 24;15(14):4591-4603. doi: 10.7150/jca.96059. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39006080 Free PMC article.
-
Causality of genetically determined metabolites on anxiety disorders: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study.J Transl Med. 2022 Oct 20;20(1):475. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03691-2. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36266699 Free PMC article.
-
No evidence of genetic causal association between sex hormone-related traits and systemic lupus erythematosus: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Clin Rheumatol. 2023 Dec;42(12):3237-3249. doi: 10.1007/s10067-023-06700-x. Epub 2023 Jul 26. Clin Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 37495778
-
Causal relationship between immune cells, inflammatory cytokines, metabolites, and erectile dysfunction: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Transl Androl Urol. 2024 Nov 30;13(11):2448-2458. doi: 10.21037/tau-24-395. Epub 2024 Nov 27. Transl Androl Urol. 2024. PMID: 39698561 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic causal relationship between age at menarche and benign oesophageal neoplasia identified by a Mendelian randomization study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 21;14:1113765. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1113765. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37025412 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O’Donnell MJ, Chin SL, Rangarajan S, Xavier D, Liu L, Zhang H, et al. . Global and regional effects of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with acute stroke in 32 countries (INTERSTROKE): a case-control study. Lancet. (2016) 388:761–75. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30506-2, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Feigin VL, Stark BA, Johnson CO, Roth GA, Bisignano C, Abady GG, et al. . Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet Neurol. (2021) 20:795–820. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00252-0, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

