Assessment of causal relationships between omega-3 and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids in autoimmune rheumatic diseases: a brief research report from a Mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 38863588
- PMCID: PMC11165037
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1356207
Assessment of causal relationships between omega-3 and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids in autoimmune rheumatic diseases: a brief research report from a Mendelian randomization study
Abstract
Background: Currently, the association between the consumption of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) and the susceptibility to autoimmune rheumatic diseases (ARDs) remains conflict and lacks substantial evidence in various clinical studies. To address this issue, we employed Mendelian randomization (MR) to establish causal links between six types of PUFAs and their connection to the risk of ARDs.
Methods: We retrieved summary-level data on six types of PUFAs, and five different types of ARDs from publicly accessible GWAS statistics. Causal relationships were determined using a two-sample MR analysis, with the IVW approach serving as the primary analysis method. To ensure the reliability of our research findings, we used four complementary approaches and conducted multivariable MR analysis (MVMR). Additionally, we investigated reverse causality through a reverse MR analysis.
Results: Our results indicate that a heightened genetic predisposition for elevated levels of EPA (ORIVW: 0.924, 95% CI: 0.666-1.283, P IVW = 0.025) was linked to a decreased susceptibility to psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Importantly, the genetically predicted higher levels of EPA remain significantly associated with an reduced risk of PsA, even after adjusting for multiple testing using the FDR method (P IVW-FDR-corrected = 0.033) and multivariable MR analysis (P MV-IVW < 0.05), indicating that EPA may be considered as the risk-protecting PUFAs for PsA. Additionally, high levels of LA showed a positive causal relationship with a higher risk of PsA (ORIVW: 1.248, 95% CI: 1.013-1.538, P IVW = 0.037). It is interesting to note, however, that the effects of these associations were weakened in our MVMR analyses, which incorporated adjustment for lipid profiles (P MV-IVW > 0.05) and multiple testing using the FDR method (P IVW-FDR-corrected = 0.062). Moreover, effects of total omega-3 PUFAs, DHA, EPA, and LA on PsA, were massively driven by SNP effects in the FADS gene region. Furthermore, no causal association was identified between the concentrations of other circulating PUFAs and the risk of other ARDs. Further analysis revealed no significant horizontal pleiotropy and heterogeneity or reverse causality.
Conclusion: Our comprehensive MR analysis indicated that EPA is a key omega-3 PUFA that may protect against PsA but not other ARDs. The FADS2 gene appears to play a central role in mediating the effects of omega-3 PUFAs on PsA risk. These findings suggest that EPA supplementation may be a promising strategy for preventing PsA onset. Further well-powered epidemiological studies and clinical trials are warranted to explore the potential mechanisms underlying the protective effects of EPA in PsA.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization study; autoimmune rheumatic diseases; omega-3; omega-6; polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Copyright © 2024 Xu, Xu, Zakeri, Wang, Yan, Wang, Li, Sun, Wang and Miao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
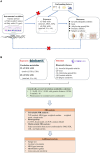
 ); (2) the instrumental variables (genetic proxies for omega-3 fatty acids, omega-6 fatty acids, EPA, DHA, LA and AA) are related to the exposure factor (solid line), and (3) the instrumental variables (genetic proxies for omega-3 fatty acids, omega-6 fatty acids, EPA, DHA, LA, and AA) are not directly related to the outcome (rheumatic diseases: Juvenile idiopathic arthritis, Gout, Ankylosing spondylitis, Psoriatic arthritis, and Sjögren syndrome) (dashed line and red
); (2) the instrumental variables (genetic proxies for omega-3 fatty acids, omega-6 fatty acids, EPA, DHA, LA and AA) are related to the exposure factor (solid line), and (3) the instrumental variables (genetic proxies for omega-3 fatty acids, omega-6 fatty acids, EPA, DHA, LA, and AA) are not directly related to the outcome (rheumatic diseases: Juvenile idiopathic arthritis, Gout, Ankylosing spondylitis, Psoriatic arthritis, and Sjögren syndrome) (dashed line and red  ). (B) Flowchart of overview of Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis.
). (B) Flowchart of overview of Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis.

Similar articles
-
Mendelian Randomization Analysis Reveals Causal Associations of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids with Sepsis and Mortality Risk.Infect Dis Ther. 2023 Jul;12(7):1797-1808. doi: 10.1007/s40121-023-00831-z. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Infect Dis Ther. 2023. PMID: 37316614 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating causal associations among gut microbiota, metabolites, and psoriatic arthritis: a Mendelian randomization study.Front Microbiol. 2024 Feb 15;15:1287637. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1287637. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38426052 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Osteoarthritis: Insights from a Mendelian Randomization Study.Nutrients. 2023 Nov 15;15(22):4787. doi: 10.3390/nu15224787. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 38004181 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic liability of gut microbiota for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and lung function: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 May 22;14:1348685. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1348685. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38841114 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Omega-3 fatty acids and autoimmune disease: Evidence from the umbrella review and Mendelian randomization analysis.Autoimmun Rev. 2024 Nov;23(11):103651. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2024.103651. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Autoimmun Rev. 2024. PMID: 39357585 Review.
Cited by
-
Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis-Associated Genes, Cytokines, and Human Leukocyte Antigens.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 May 16;60(5):815. doi: 10.3390/medicina60050815. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38792999 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

