Placebo effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on negative symptoms and cognition in patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38863608
- PMCID: PMC11165700
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1377257
Placebo effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on negative symptoms and cognition in patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Negative symptoms and cognitive impairments are highly frequent in schizophrenia spectrum disorders (SSD), associated with adverse functional outcomes and quality of life. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) has been considered a promising therapeutic option in SSD. However, placebo effects of rTMS on these symptoms remained unclear.
Objective: To investigate placebo effects of rTMS on alleviating negative symptoms and cognitive impairment in patients with SSD and to explore potential moderators.
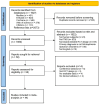
Methods: We systematically searched five electronic databases up to 15 July 2023. Randomized, double-blind, sham-controlled trials investigating effects of rTMS on negative symptoms or cognition in patients with SSD were included. The pooled placebo effect sizes, represented by Hedges' g, were estimated using the random-effects model. Potential moderators were explored through subgroup analysis and meta-regression.
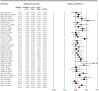
Results: Forty-four randomized controlled trials with 961 patients (mean age 37.53 years; 28.1% female) in the sham group were included. Significant low-to-moderate pooled placebo effect sizes were observed for negative symptoms (g=0.44, p<0.001), memory (g=0.31, p=0.010), executive function (g=0.35, p<0.001), working memory (g=0.26, p=0.004), and processing speed (g=0.36, p=0.004). Subgroup analysis indicated that placebo effects were affected by sham stimulation methods, rTMS targeting approaches, and stimulation frequency.
Conclusions: Placebo effects of rTMS on negative symptoms and cognition in patients with SSD are significant in a small-to-moderate magnitude, which might be mediated by rTMS parameters. Our findings will provide new insights for practitioners to further optimize and establish standardized rTMS protocols for future RCTs tackling cardinal symptoms in SSD.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, identifier CRD42023390138.
Keywords: cognition; negative symptoms; placebo effects; randomized controlled trial; repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation; schizophrenia spectrum disorders.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Lu, Hao, Xia, Shi and Su.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Patients With Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Front Hum Neurosci. 2021 Oct 26;15:723715. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.723715. eCollection 2021. Front Hum Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34764859 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation Does Not Improve Working Memory in Schizophrenia: A Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials.Neuropsychol Rev. 2021 Mar;31(1):115-138. doi: 10.1007/s11065-020-09454-4. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Neuropsychol Rev. 2021. PMID: 32918254
-
Comparative Efficacy of Different Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Protocols for Stroke: A Network Meta-Analysis.Front Neurol. 2022 Jun 15;13:918786. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.918786. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35785350 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for subjective chronic tinnitus: a randomized controlled trial meta-analysis.Front Neurosci. 2025 Apr 15;19:1579846. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1579846. eCollection 2025. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40303608 Free PMC article.
-
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation combined with cognitive training for cognitive function and activities of daily living in patients with post-stroke cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Ageing Res Rev. 2023 Jun;87:101919. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2023.101919. Epub 2023 Mar 31. Ageing Res Rev. 2023. PMID: 37004840
Cited by
-
Evaluating the Therapeutic Efficacy of rTMS Combined with Low-Dose Antipsychotic Medication in Somatic Symptom Disorder.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2025 Jul 3;21:1315-1324. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S518025. eCollection 2025. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2025. PMID: 40625879 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of theta burst stimulation on cognitive function and characteristics of blood oxygen alterations based on near-infrared spectroscopy in chronic schizophrenia.BMC Psychiatry. 2025 Aug 12;25(1):784. doi: 10.1186/s12888-025-07240-1. BMC Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40797243 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

