Clinical value of serum tumor markers in assessing the efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in advanced ovarian cancer: single-center prospective clinical study
- PMID: 38863620
- PMCID: PMC11165076
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1399502
Clinical value of serum tumor markers in assessing the efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in advanced ovarian cancer: single-center prospective clinical study
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to assess the clinical importance of various biomarkers, including NLR, CEA, CA199, CA125, CA153, and HE4, through dynamic testing to evaluate the effectiveness of neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) for individuals facing advanced ovarian cancer. This provides valuable information for tailoring treatment plans to individual patients, thereby leading to a more personalized and effective management of individuals facing ovarian cancer.
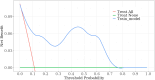
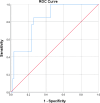
Methods: The levels of NLR, CA125, CA199, CEA, CA153, and HE4 were detected before chemotherapy and after 3 courses of chemotherapy. Patients were categorized into ineffective and effective groups according to the effectiveness of NACT. To evaluate the factors influencing NACT's effectiveness in individuals facing advanced ovarian cancer, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, predictive modeling, and multifactorial regression analysis were employed.
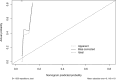
Results: In the effective group, the patients' age, maximum tumor diameter, and CEA and HE4 levels of the patients were significantly higher compared to those in the ineffective group (P <.05). Additionally, the difference in HE4 levels before and after treatment between the effective and ineffective groups was statistically significant (P<.05). Multifactorial analysis showed that age and maximum tumor diameter were independent risk factors impacting the effectiveness of NACT in individuals facing advanced ovarian cancer (P<.05). The ROC curve for predicting the effectiveness of NACT in individuals facing advanced ovarian cancer showed a sensitivity of 93.3% for NLR and a specificity of 92.3% for CA199. HE4 emerged as the most reliable predictor, demonstrating a specificity of 84.6% and a sensitivity of 75.3%. The area under the curve of the combined CA125 and HE4 assays for predicting the ineffectiveness of NACT in individuals facing advanced ovarian cancer was 0.825, showcasing a specificity of 74.2% and a sensitivity of 84.6%.
Conclusion: The predictive capacity for the effectiveness of NACT in individuals facing advanced ovarian cancer is notably high when considering the sensitivity of NLR and the specificity of CA199. Additionally, the combination of CA125 and HE4 assays can obtain a better predictive effect, which can accurately select patients suitable for NACT, determine the appropriate timing of the interval debulking surgery (IDS) surgery, and achieve a satisfactory tumor reduction effect.
Keywords: efficacy of chemotherapy; human epididymal protein 4; neoadjuvant chemotherapy; ovarian cancer; predictive indicators.
Copyright © 2024 Huang, Du, Chen, Luo, Wang, Li, Li and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Serum HE4 superior to CA125 in predicting poorer surgical outcome of epithelial ovarian cancer.Tumour Biol. 2016 Nov;37(11):14765-14772. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5335-0. Epub 2016 Sep 15. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27629144
-
Serum HE4 and CA125 as predictors of response and outcome during neoadjuvant chemotherapy of advanced high-grade serous ovarian cancer.Tumour Biol. 2014 Dec;35(12):12389-95. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2553-1. Epub 2014 Sep 5. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 25190018
-
Kinetics of HE4 and CA125 as prognosis biomarkers during neoadjuvant chemotherapy in advanced epithelial ovarian cancer.J Ovarian Res. 2021 Jul 19;14(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s13048-021-00845-6. J Ovarian Res. 2021. PMID: 34275472 Free PMC article.
-
[Analysis of factors related to the prognostic benefit of neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by interval debulking surgery in patients with advanced ovarian cancer].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2021 Jun 25;56(6):385-392. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112141-20201207-00871. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34154313 Chinese.
-
Construction of a nomogram model for predicting the outcome of debulking surgery for ovarian cancer on the basis of clinical indicators.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 10;14:1421247. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1421247. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39050577 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrative approach for enhanced ovarian cancer diagnosis: cytology and biomarkers.Discov Oncol. 2025 Aug 10;16(1):1519. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-03231-6. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40784922 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

