Pediatric schwannoma of the hypoglossal nerve: a case report and narrative literature overview
- PMID: 38863642
- PMCID: PMC11165051
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1400335
Pediatric schwannoma of the hypoglossal nerve: a case report and narrative literature overview
Abstract
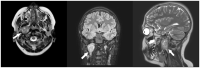
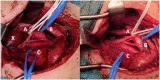
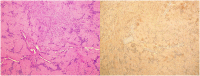
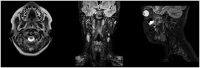
Schwannomas are benign, slow-growing tumors originating from the Schwann cells of nerve sheaths. Extracranial schwannomas are rare, particularly in pediatric populations. Here, we report the case of a hypoglossal schwannoma in a 15-year-old male who experienced tongue paresthesia and fasciculations and difficulty swallowing two years before hospital admission. Magnetic resonance imaging showed an oval mass with sharp and regular limits of approximately 45 × 29 × 25 mm in the cranial portion of the right carotid adipose space, caudal to the right carotid and lateral foramen. The patient underwent surgery, and a histological examination confirmed a schwannoma of the hypoglossal nerve. Six months after surgery, the patient was symptom-free. The literature on schwannomas of the hypoglossal nerve is scarce, with only a few previously reported cases in the adult population. Despite their rarity, schwannomas should be considered in the differential diagnosis of masses located in the neck that present with lingual and occasionally auditory symptoms, even in pediatric patients. Surgical resection is recommended and has a low risk of long-term recurrence.
Keywords: hypoglossal schwannoma; management; neck masses; pediatric schwannoma; tongue disease.
Copyright © 2024 Marcandella, Boscarelli, Murru, Abbracciavento, Spazzapan and Schleef.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypoglossal Schwannoma of Neck: Case Report and Review of Literature.World Neurosurg. 2018 Feb;110:240-243. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2017.11.069. Epub 2017 Nov 22. World Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 29175571 Review.
-
Schwannoma of the descending loop of the hypoglossal nerve: case report.Pan Afr Med J. 2020 Jun 8;36:73. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2020.36.73.23500. eCollection 2020. Pan Afr Med J. 2020. PMID: 32774632 Free PMC article.
-
Solid-Cystic Hypoglossal Nerve Schwannoma with Fluid-Fluid Level: A Rare Case Report.J Clin Diagn Res. 2016 Dec;10(12):TD06-TD08. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2016/23337.9094. Epub 2016 Dec 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016. PMID: 28208975 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoglossal Nerve Schwannoma: Case Report and Literature Review.World Neurosurg. 2020 Mar;135:205-208. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.12.006. Epub 2019 Dec 9. World Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 31821912 Review.
-
Hypoglossal schwannoma of parapharyngeal space: an unusual case report.J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2015 Mar;14(Suppl 1):73-6. doi: 10.1007/s12663-011-0308-8. Epub 2011 Oct 22. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2015. PMID: 25838673 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Martel T, Subirana A, Guillaume J. Voluminoso neurinoma del hipogloso con desarrollo juxta-bulboprotuberancial. Ars Medica. (1933) 9:416–9.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

