Robotic distal gastrectomy using a novel pre-emptive supra-pancreatic approach without duodenal transection in the dissection of D2 lymph nodes for gastric cancer
- PMID: 38863643
- PMCID: PMC11165139
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1388626
Robotic distal gastrectomy using a novel pre-emptive supra-pancreatic approach without duodenal transection in the dissection of D2 lymph nodes for gastric cancer
Abstract
Background: Robot-assisted surgery has shown remarkable progress as a minimally invasive procedure for gastric cancer. This study aimed to compare the pre-emptive suprapancreatic approach without duodenal transection and the conventional approach in terms of perioperative feasibility and short-term surgical outcomes.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed all patients who underwent robotic distal gastrectomy with D2 lymph node dissection using the da Vinci Xi robotic system between December 2021 and April 2023 and categorized them into two groups for comparison. Patients treated using the pre-emptive suprapancreatic approach (observation group) were compared with those who received the conventional approach (control group). Employing one-to-one propensity score matching, we evaluated the postoperative morbidity and short-term outcomes in these two distinct groups to assess the efficacy and safety of the novel surgical technique.
Results: This study enrolled 131 patients: 70 in the observation group and 61 in the control group. After propensity score matching, the operative times were significantly longer in the control group than in the observation group (229.10 ± 33.96 vs. 174.84 ± 18.37, p <0.001). The mean blood loss was lower in the observation group than in the control group (25.20 ± 11.18 vs. 85.00 ± 38.78, p <0.001). Additionally, the observation group exhibited a higher number of retrieved lymph nodes, including suprapyloric, perigastric, and superior pancreatic lymph nodes (28.69 ± 5.48 vs. 19.21 ± 2.89, p <0.001; 4.98 ± 1.27 vs. 4.29 ± 1.21, p = 0.012; 10.52 ± 2.39 vs. 5.50 ± 1.62, p <0.001; 6.26 ± 2.64 vs. 5.00 ± 1.72, p = 0.029). Drain amylase levels in the observation group were significantly lower than those in the control group (30.08 ± 33.74 vs. 69.14 ± 66.81, p <0.001).
Conclusion: This study revealed that using the pre-emptive suprapancreatic approach without duodenal transection in the dissection of D2 lymph nodes for gastric cancer is a safe and feasible procedure in terms of surgical outcomes.
Keywords: gastric cancer; gastrointestinal surgery; lymph node dissection; pre-emptive supra-pancreatic approach; robotic distal gastrectomy.
Copyright © 2024 Xie, Yang, Wang, Yin and Yan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
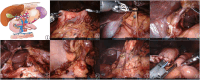
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Comparison of short-term efficacy between robotic and 3D laparoscopic-assisted D2 radical distal gastrectomy for gastric cancer].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Apr 25;23(4):350-356. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn.441530-20200224-00085. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32306602 Chinese.
-
An Optimal Surgical Approach for Suprapancreatic Area Dissection in Laparoscopic D2 Gastrectomy with Complete Mesogastric Excision.J Gastrointest Surg. 2020 Apr;24(4):916-917. doi: 10.1007/s11605-019-04467-8. Epub 2020 Jan 2. J Gastrointest Surg. 2020. PMID: 31898108
-
Reduced-port robotic radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer: a single-institute experience.BMC Surg. 2022 May 19;22(1):198. doi: 10.1186/s12893-022-01645-5. BMC Surg. 2022. PMID: 35590316 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of laparoscopy-assisted by conventional open distal gastrectomy and extraperigastric lymph node dissection in early gastric cancer.J Surg Oncol. 2005 Jul 1;91(1):90-4. doi: 10.1002/jso.20271. J Surg Oncol. 2005. PMID: 15999352 Review.
-
Effect of indocyanine green near-infrared light imaging technique guided lymph node dissection on short-term clinical efficacy of minimally invasive radical gastric cancer surgery: a meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2023 Sep 11;13:1257585. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1257585. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37766867 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhou T, Wu L, Ma N, Tang F, Chen J, Jiang Z, et al. . Photothermally responsive theranostic nanocomposites for near-infrared light triggered drug release and enhanced synergism of photothermo-chemotherapy for gastric cancer. Bioeng Transl Med. (2022) 8(1):e10368. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10368 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

