Health-related quality of life in adults with hematological cancer: a 2023 cross-sectional survey from Qatar
- PMID: 38863644
- PMCID: PMC11165142
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1391429
Health-related quality of life in adults with hematological cancer: a 2023 cross-sectional survey from Qatar
Abstract
Background: Hematological cancers impose a complex burden on individuals, affecting their physical health and mental and emotional well-being. This study evaluated the health-related Quality of Life (HRQOL) and its determinants among adults with hematological cancers in Qatar in 2023.
Methods: A cross-sectional study used a validated structured questionnaire conducted among adult patients diagnosed with hematological cancers. All adult patients who attended The National Centre for Cancer Care and Research (NCCCR) in Qatar during the Data collection period (January to March 2023) and agreed to participate were included in the study.
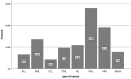
Results: A total of 257 participants were enrolled in the study. The highest median (IQR) score of the HRQOL domain was observed in the functionating score of 90.6 (13.8), followed by the global health score of 83.3(25. 0). The median (IQR) of the symptoms burden score was 07.4(12.3). Gender significantly affects HRQOL, with males reporting better functioning and lower symptom burden than females. Employment status is positively associated with functioning scores. Regular exercise correlates with higher global health and functioning scores and lower symptom burden, while depressive symptoms are linked to poorer HRQOL outcomes. Patients experiencing cancer recurrence or active disease report lower global health and functioning scores and higher symptom burden. Treatment modalities such as chemotherapy and bone marrow transplant (BMT) timing also influence HRQOL, with recent treatment recipients showing lower global health and higher symptom burden scores. Depressive symptoms were the primary factor, lowering the global health score by 15.2%. Regarding the low functioning score predictors, female gender, depressive symptoms, and cancer recurrence emerged as significant predictors of the low functioning score. Furthermore, Regular exercise increased the functioning score by 03.4 units (p-value=0.018). Finally, Multiple linear regression analysis reinforced the significance of depressive symptoms, active disease status, and recurrence within the past five years as substantial predictors of higher symptom scores.
Conclusions: The study emphasizes the profound impact of depressive symptoms on all aspects of Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQOL), mainly affecting global health. It highlights the positive role of regular exercise in enhancing global health, functioning, and symptom burden scores.
Keywords: blood cancer; depressive symptoms; health-related quality of life; hematological cancer; quality of life.
Copyright © 2024 Abdu, Ahmed, Abdou, Elhussein, Sirelkhatim, Bougmiza, Yassin and Selim.
Conflict of interest statement
YA, MA and MY were employed by Hamad Medical Corporation. IB and NS were employed by Primary Health Care Corporation. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Health-related quality of life in ovarian cancer survivors: Results from the American Cancer Society's Study of Cancer Survivors - I.Gynecol Oncol. 2016 Jun;141(3):543-549. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2016.04.006. Epub 2016 Apr 19. Gynecol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27072805 Free PMC article.
-
The Humanistic and Economic Burden Associated with Major Depressive Disorder: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Analysis.Adv Ther. 2024 May;41(5):1860-1884. doi: 10.1007/s12325-024-02817-w. Epub 2024 Mar 11. Adv Ther. 2024. PMID: 38466558 Free PMC article.
-
Perceived Health and Quality of Life in Patients With CKD, Including Those With Kidney Failure: Findings From National Surveys in France.Am J Kidney Dis. 2020 Jun;75(6):868-878. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.08.026. Epub 2019 Dec 23. Am J Kidney Dis. 2020. PMID: 31879215
-
Symptom burden and health-related quality of life in chronic kidney disease: A global systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS Med. 2022 Apr 6;19(4):e1003954. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003954. eCollection 2022 Apr. PLoS Med. 2022. PMID: 35385471 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise training for advanced lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Feb 11;2(2):CD012685. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012685.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30741408 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hematology ASo. blood cancers (2023). Available online at: https://www.hematology.org/education/patients/blood-cancers.
-
- international agency for research on cancer . W. leukemia (2020). Available online at: file:///C:/Users/drelh/Downloads/36-Leukaemia-fact-sheet.pdf.
-
- leukemia and lymphoma society. facts and statistics overview (2021). Available online at: https://www.lls.org/facts-and-statistics/facts-and-statistics-overview.
-
- Saudi Cancer Registry . Cancer Incidence Report (2014). Available online at: https://nhic.gov.sa/eServices/Documents/2014.pdf.
-
- World health organization . international agency for research on cancer (2021). Available online at: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/populations/634-Qatar-fact-she....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

