Transarterial chemoembolization combined with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab conversion therapy for intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: a case report and literature review
- PMID: 38863699
- PMCID: PMC11165049
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1358602
Transarterial chemoembolization combined with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab conversion therapy for intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: a case report and literature review
Abstract
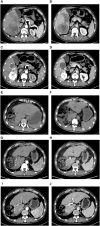
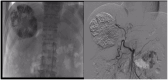
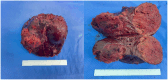
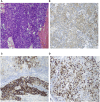
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) ranks as the sixth most common malignancy globally, with the majority of patients presenting at the initial diagnosis with locally advanced or metastatic disease, precluding the opportunity for curative surgical intervention. With the exploration and advancement of locoregional treatments, novel molecular-targeted therapies, anti-angiogenic agents, and immunomodulatory drugs, the management of HCC has seen an increase in objective response rates and prolonged duration of response significantly enhancing the potential for conversion to resectable disease in intermediate and advanced-stage unresectable HCC. Herein, we present a case of Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage B unresectable HCC, where after two courses of treatment with transarterial chemoembolization combined with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab significant tumor reduction was achieved. Per Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors 1.1, partial response culminated in successful curative surgical resection. No drug-related adverse reactions occurred during hospitalization, and there has been no recurrence during the 11-month postoperative follow-up. For patients with Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage B (intermediate-stage) unresectable HCC, the transarterial chemoembolization combined with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab regimen may offer improved therapeutic outcomes leading to a higher success rate of conversion therapy and, thus, improved survival.
Keywords: atezolizumab plus bevacizumab; conversion therapy; immunotherapy; intermediate-stage unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma; transarterial chemoembolization.
Copyright © 2024 Ai, Gong, Ma, Ma, Ding, Ding, Wang and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
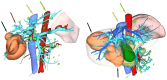
Similar articles
-
Protocol of the IMPACT study: randomized, multicenter, phase 3 study evaluating the efficacy of immunotherapy (Atezolizumab) plus anti-VEGF therapy (Bevacizumab) in combination with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2025 Mar 11;25(1):434. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13648-5. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40069616 Free PMC article.
-
Atezolizumab and bevacizumab plus transarterial chemoembolization and hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for patients with high tumor burden unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A multi-center cohort study.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Sep 30;139:112711. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112711. Epub 2024 Jul 18. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39029233
-
Three effective cases of transcatheter arterial embolization after atezolizumab and bevacizumab treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2025 Jan 27;19(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s13256-025-05040-5. J Med Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 39871286 Free PMC article.
-
Combination therapies plus transarterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma: a snapshot of clinical trial progress.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2022 Apr;31(4):379-391. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2022.2008355. Epub 2021 Nov 25. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2022. PMID: 34788184 Review.
-
Successful radical surgery for lymph node metastasis in a patient with hepatocellular carcinoma following atezolizumab plus bevacizumab combination therapy: a case report and literature review.Clin J Gastroenterol. 2024 Dec;17(6):1067-1074. doi: 10.1007/s12328-024-02032-8. Epub 2024 Aug 20. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39162953 Review.
Cited by
-
Conversion study of hepatocellular carcinoma using HAIC combined with lenvatinib and PD-1/L1 immunotherapy under the guidance of BCLC staging.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 2;16:1596864. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1596864. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40529364 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

