Integrated bioinformatics combined with machine learning to analyze shared biomarkers and pathways in psoriasis and cervical squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 38863714
- PMCID: PMC11165063
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1351908
Integrated bioinformatics combined with machine learning to analyze shared biomarkers and pathways in psoriasis and cervical squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Psoriasis extends beyond its dermatological inflammatory manifestations, encompassing systemic inflammation. Existing studies have indicated a potential risk of cervical cancer among patients with psoriasis, suggesting a potential mechanism of co-morbidity. This study aims to explore the key genes, pathways, and immune cells that may link psoriasis and cervical squamous cell carcinoma (CESC).
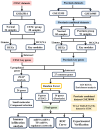
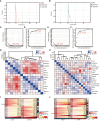
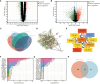
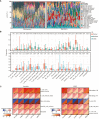
Methods: The cervical squamous cell carcinoma dataset (GSE63514) was downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO). Two psoriasis-related datasets (GSE13355 and GSE14905) were merged into one comprehensive dataset after removing batch effects. Differentially expressed genes were identified using Limma and co-expression network analysis (WGCNA), and machine learning random forest algorithm (RF) was used to screen the hub genes. We analyzed relevant gene enrichment pathways using GO and KEGG, and immune cell infiltration in psoriasis and CESC samples using CIBERSORT. The miRNA-mRNA and TFs-mRNA regulatory networks were then constructed using Cytoscape, and the biomarkers for psoriasis and CESC were determined. Potential drug targets were obtained from the cMAP database, and biomarker expression levels in hela and psoriatic cell models were quantified by RT-qPCR.
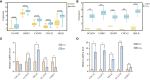
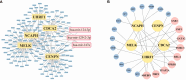
Results: In this study, we identified 27 key genes associated with psoriasis and cervical squamous cell carcinoma. NCAPH, UHRF1, CDCA2, CENPN and MELK were identified as hub genes using the Random Forest machine learning algorithm. Chromosome mitotic region segregation, nucleotide binding and DNA methylation are the major enrichment pathways for common DEGs in the mitotic cell cycle. Then we analyzed immune cell infiltration in psoriasis and cervical squamous cell carcinoma samples using CIBERSORT. Meanwhile, we used the cMAP database to identify ten small molecule compounds that interact with the central gene as drug candidates for treatment. By analyzing miRNA-mRNA and TFs-mRNA regulatory networks, we identified three miRNAs and nine transcription factors closely associated with five key genes and validated their expression in external validation datasets and clinical samples. Finally, we examined the diagnostic effects with ROC curves, and performed experimental validation in hela and psoriatic cell models.
Conclusions: We identified five biomarkers, NCAPH, UHRF1, CDCA2, CENPN, and MELK, which may play important roles in the common pathogenesis of psoriasis and cervical squamous cell carcinoma, furthermore predict potential therapeutic agents. These findings open up new perspectives for the diagnosis and treatment of psoriasis and squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix.
Keywords: biomarkers; cervical squamous cell carcinoma (CESC); immune cell infiltration; machine learning; psoriasis.
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Yin, Yang, Zhang, Wu, Zheng, Wu and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification and validation of shared biomarkers and drug repurposing in psoriasis and Crohn's disease: integrating bioinformatics, machine learning, and experimental approaches.Front Immunol. 2025 May 8;16:1587705. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1587705. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40406126 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated analysis of key microRNAs /TFs /mRNAs/ in HPV-positive cervical cancer based on microRNA sequencing and bioinformatics analysis.Pathol Res Pract. 2020 Jun;216(6):152952. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2020.152952. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Pathol Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 32307200
-
Prediction of a miRNA-mRNA functional synergistic network for cervical squamous cell carcinoma.FEBS Open Bio. 2019 Dec;9(12):2080-2092. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12747. Epub 2019 Nov 17. FEBS Open Bio. 2019. PMID: 31642613 Free PMC article.
-
Common gene signatures and key pathways in hypopharyngeal and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Evidence from bioinformatic analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Oct 16;99(42):e22434. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022434. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33080677 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics and machine learning approaches reveal key genes and underlying molecular mechanisms of atherosclerosis: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Aug 2;103(31):e38744. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038744. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39093811 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and validation of shared biomarkers and drug repurposing in psoriasis and Crohn's disease: integrating bioinformatics, machine learning, and experimental approaches.Front Immunol. 2025 May 8;16:1587705. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1587705. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40406126 Free PMC article.
-
Pan-cancer analysis and single-cell analysis identifies the CENPN as a biomarker for survival prognosis and immunotherapy.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jan 17;16(1):55. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-01801-2. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39832113 Free PMC article.
-
NLRP3-inflammasome Related Genes as Emerging Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets in Psoriasis.Inflammation. 2025 Mar 3. doi: 10.1007/s10753-025-02271-y. Online ahead of print. Inflammation. 2025. PMID: 40029502
-
Exploring immune-inflammation markers in psoriasis prediction using advanced machine learning algorithms.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 31;16:1619490. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1619490. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40821804 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric analysis of research on cervical cancer and miRNAs from 2010 to 2024: research trends, hotspots, and prospects.Discov Oncol. 2025 Aug 27;16(1):1639. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-03106-w. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40864203 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blauvelt A, Lebwohl M, Langley RG, Rowland K, Yang YW, Chan D, et al. . Malignancy rates through 5 years of follow-up in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis treated with guselkumab: Pooled results from the VOYAGE 1 and VOYAGE 2 trials. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2023) 89:274–82. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2023.03.035 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

