Intraoperative Dexmedetomidine for Prevention of Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction and Delirium in Elderly Patients with Lobectomy: A Propensity Score-Matched, Retrospective Study
- PMID: 38863738
- PMCID: PMC11166154
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S456762
Intraoperative Dexmedetomidine for Prevention of Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction and Delirium in Elderly Patients with Lobectomy: A Propensity Score-Matched, Retrospective Study
Abstract
Purpose: This study aims to investigate whether dexmedetomidine could prevent postoperative cognitive dysfunction and delirium in patients with lobectomy.
Patients and methods: Patients with lung cancer who underwent thoracoscopic lobectomy under general anesthesia were enrolled in this study and divided into dexmedetomidine group or control group. Propensity-score match (PSM) was used to reduce the bias and imbalance of confounding variables. After PSM, 87 patients in each group were included. Primary outcomes were postoperative cognitive function and delirium. Secondary outcomes include plasma TNF-α, IL-6, and S100 β protein concentrations. Adverse events were also collected.
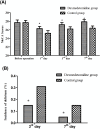
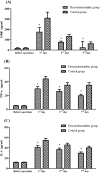
Results: There were no significant differences in the demographic characteristics and hemodynamic parameters between the two groups. Compared with the control group, the MoCA scores were significantly higher (P<0.01), while the incidence of delirium (P<0.01) and the plasma TNF-α (P<0.01), IL-6 (P<0.01), and S100 β protein (P<0.01) concentrations were significantly lower in the dexmedetomidine group at 7 days post-operatively. The incidences of adverse events were similar between the two groups.
Conclusion: Dexmedetomidine could prevent postoperative cognitive dysfunction and delirium in patients with lobectomy by decreasing neuroinflammation.
Keywords: Dexmedetomidine; cognitive dysfunction; inflammation; pneumonectomy; postoperative cognitive complications.
© 2024 Tang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevention of dexmedetomidine on postoperative delirium and early postoperative cognitive dysfunction in elderly patients undergoing hepatic lobectomy.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Feb 28;47(2):219-225. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2022.210280. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 35545412 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. Chinese, English.
-
Role of dexmedetomidine in reducing the incidence of postoperative cognitive dysfunction caused by sevoflurane inhalation anesthesia in elderly patients with esophageal carcinoma.J Cancer Res Ther. 2018;14(7):1497-1502. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_164_18. J Cancer Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 30589029
-
Intraoperative dexmedetomidine for prevention of postoperative delirium in elderly patients with mild cognitive impairment.Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2021 Jan;36(1):143-151. doi: 10.1002/gps.5406. Epub 2020 Nov 10. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33411362
-
Dexmedetomidine in Prevention of Postoperative Delirium: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2022 Jun 3;14(6):e25639. doi: 10.7759/cureus.25639. eCollection 2022 Jun. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35812638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness of dexmedetomidine on postoperative cognitive dysfunction in elderly patients with fracture: A systematic review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Mar 17;102(11):e31749. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000031749. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 36930077 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of dexmedetomidine on early postoperative cognitive function and postoperative inflammatory response: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2024 Aug 12;15:1422049. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1422049. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39188709 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Dexmedetomidine or Propofol on Postoperative Oxygenation Index During Invasive Ventilation in Patients After off-Pump Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting: a Single-Center Retrospective Study.Int J Gen Med. 2025 Jun 27;18:3463-3476. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S524691. eCollection 2025. Int J Gen Med. 2025. PMID: 40607013 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harris CG, James RS, Tian DH, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of uniportal versus multiportal video-assisted thoracoscopic lobectomy for lung cancer. Ann Cardiothorac Surg. 2016;5(2):76–84. PubMed PMID: 27134832; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4827401. doi:10.21037/acs.2016.03.17 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Moller JT, Cluitmans P, Rasmussen LS, et al. Long-term postoperative cognitive dysfunction in the elderly ISPOCD1 study. ISPOCD investigators. International Study of Post-Operative Cognitive Dysfunction. Lancet. 1998;351(9106):857–861. PubMed PMID: 9525362. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(97)07382-0 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

