Effects of Ankle Compression Garments on Fatigue and Single-Leg Balance in Collegiate Basketball Players
- PMID: 38863788
- PMCID: PMC11166133
- DOI: 10.70252/YHDY9251
Effects of Ankle Compression Garments on Fatigue and Single-Leg Balance in Collegiate Basketball Players
Abstract
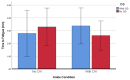
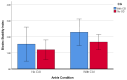
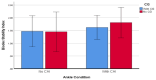
Basketball players are prone to ankle injuries. It is unclear if wearing ankle compression garments (CGs) can enhance balance control and time to fatigue in those athletes. The purpose of this study was to examine the impact of ankle CGs on both time to fatigue and single-leg balance. Sixteen Division II (D2) collegiate basketball players participated in the study. The Cumberland Ankle Instability Tool (CAIT) was used to assess ankle stability. Fatigue was induced through deficit heel raises, and single-leg balance was assessed with the Athletic Single Leg Stability Test (ASLST) of the Biodex Balance System. Ten out of 16 (62.5%) basketball players were classified as having chronic ankle instability (CAI). Wearing CGs did not significantly prolong the time to fatigue (P = .774), and participants with CAI and without CAI had a similar time to fatigue (P = .958). In addition, wearing CGs significantly worsened single-leg balance before fatigue (P = .021), but enhanced balance control after fatigue (P = .027). Results indicate a strong prevalence of CAI in collegiate basketball players, and wearing CGs may not be able to enhance single-leg balance before fatigue. Although participants who wore CGs did not significantly increase their time to fatigue, their single-leg balance significantly improved after fatigue. This finding suggests wearing ankle CGs may have the potential to remediate the impact of fatigue on balance control. Future studies with a larger sample size are needed to further examine the impact of wearing ankle CGs on fatigue and single-leg balance.
Keywords: Chronic ankle instability; balance; basketball; compression garment.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ankle Stability and Single-Leg Balance Control in Collegiate Female Soccer Players versus Non-Soccer Players.Int J Exerc Sci. 2024 Dec 1;17(6):1406-1415. doi: 10.70252/CQMP3296. eCollection 2024. Int J Exerc Sci. 2024. PMID: 39807291 Free PMC article.
-
Bilateral symmetry of vertical time to stabilization in postural sway after double-leg landing in elite athletes with unilateral chronic ankle sprain.J Foot Ankle Res. 2022 May 31;15(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s13047-022-00552-5. J Foot Ankle Res. 2022. PMID: 35641968 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Hop-Stabilization Training on Ankle Instability and Function of Adolescent Female Basketball Players with Chronic Ankle Instability: A Double-Blind, Prospective, Cluster-Randomized Controlled Trial.J Clin Med. 2025 May 16;14(10):3502. doi: 10.3390/jcm14103502. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40429497 Free PMC article.
-
Compression garments and exercise: garment considerations, physiology and performance.Sports Med. 2011 Oct 1;41(10):815-43. doi: 10.2165/11591420-000000000-00000. Sports Med. 2011. PMID: 21923201 Review.
-
The Effects of Lower Leg Compression Garments on Lower Extremity Sports Injuries, Subjective Fatigue and Biomechanical Variables: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis.Int J Exerc Sci. 2024 Apr 1;17(6):445-467. doi: 10.70252/VBVG7314. eCollection 2024. Int J Exerc Sci. 2024. PMID: 38665681 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rebuilding Stability: Exploring the Best Rehabilitation Methods for Chronic Ankle Instability.Sports (Basel). 2024 Oct 17;12(10):282. doi: 10.3390/sports12100282. Sports (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39453248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of different pressure midfoot wraps on balance and proprioception in amateur basketball athletes.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 May 23;13:1560522. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1560522. eCollection 2025. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40486203 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arifin N, Abu Osman NA, Wan Abas WA. Intrarater test-retest reliability of static and dynamic stability indexes measurement using the Biodex Stability System during unilateral stance. J Appl Biomech. 2014;30(2):300–304. - PubMed
-
- Banfi G, Colombini A, Lombardi G, Lubkowska A. Metabolic markers in sports medicine. Adv Clin Chem. 2012;56:1–54. - PubMed
-
- Borg GA. Psychophysical bases of perceived exertion. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1982;14(5):377–381. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
