Cross-species signaling pathways analysis inspire animal model selections for drug screening and target prediction in vascular aging diseases
- PMID: 38863828
- PMCID: PMC11164676
- DOI: 10.1111/eva.13708
Cross-species signaling pathways analysis inspire animal model selections for drug screening and target prediction in vascular aging diseases
Abstract
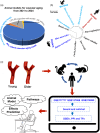
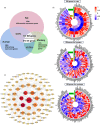
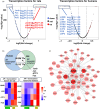
Age is a significant contributing factor to the occurrence and progression of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Pharmacological treatment can effectively alleviate CVD symptoms caused by aging. However, 90% of the drugs have failed in clinics because of the loss of drug effects or the occurrence of the side effects. One of the reasons is the disparity between animal models used and the actual physiological levels in humans. Therefore, we integrated multiple datasets from single-cell and bulk-seq RNA-sequencing data in rats, monkeys, and humans to identify genes and pathways with consistent/differential expression patterns across these three species. An approach called "Cross-species signaling pathway analysis" was developed to select suitable animal models for drug screening. The effectiveness of this method was validated through the analysis of the pharmacological predictions of four known anti-vascular aging drugs used in animal/clinical experiments. The effectiveness of drugs was consistently observed between the models and clinics when they targeted pathways with the same trend in our analysis. However, drugs might have exhibited adverse effects if they targeted pathways with opposite trends between the models and the clinics. Additionally, through our approach, we discovered four targets for anti-vascular aging drugs, which were consistent with their pharmaceutical effects in literatures, showing the value of this approach. In the end, software was established to facilitate the use of "Cross-species signaling pathway analysis." In sum, our study suggests utilizing bioinformatics analysis based on disease characteristics can help in choosing more appropriate animal models.
Keywords: animal model; cross‐species signaling pathway analysis; drugs in research; single‐cell RNA‐seq; vascular aging.
© 2024 The Author(s). Evolutionary Applications published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Efficacy of Renshen Sanqi Chuanxiong formula for preventing vascular aging.J Tradit Chin Med. 2019 Dec;39(6):780-793. J Tradit Chin Med. 2019. PMID: 32186148
-
Large-scale phenotypic drug screen identifies neuroprotectants in zebrafish and mouse models of retinitis pigmentosa.Elife. 2021 Jun 29;10:e57245. doi: 10.7554/eLife.57245. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34184634 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of molecular networks and targets mining of Chinese herbal medicines on anti-aging.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Dec 28;16(1):520. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1513-2. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 28031022 Free PMC article.
-
[Aiming for zero blindness].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2015 Mar;119(3):168-93; discussion 194. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2015. PMID: 25854109 Review. Japanese.
-
Health Benefits of Anti-aging Drugs.Subcell Biochem. 2019;91:339-392. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-3681-2_13. Subcell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30888659 Review.
References
-
- Alastair Stewart, D. D. , Gao, X. , & Toh, Y.‐C. (2023). The FDA modernisation act 2.0: Bringing non‐animal technologies to the regulatory table. Drug Discovery Today, 28, 103496. - PubMed
-
- Baptista, C. V. J. , Faustino‐Rocha, A. I. , & Oliveira, P. A. (2021). Animal models in pharmacology: A brief history awarding the Nobel prizes for physiology or medicine. Pharmacology, 106, 356–368. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin, E. J. , Blaha, M. J. , Chiuve, S. E. , Cushman, M. , Das, S. R. , Deo, R. , de Ferranti, S. D. , Floyd, J. , Fornage, M. , Gillespie, C. , Isasi, C. R. , Jiménez, M. C. , Jordan, L. C. , Judd, S. E. , Lackland, D. , Lichtman, J. H. , Lisabeth, L. , Liu, S. , Longenecker, C. T. , … American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee . (2017). Heart disease and stroke statistics‐2017 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation, 135, e146–e603. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blondel, V. D. , Guillaume, J. L. , Lambiotte, R. , & Lefebvre, E. (2008). Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. Journal of Statistical Mechanics: Theory and Experiment, 2008, P10008.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

