Diagnostic potential of TSH to HDL cholesterol ratio in vulnerable carotid plaque identification
- PMID: 38863898
- PMCID: PMC11166198
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1333908
Diagnostic potential of TSH to HDL cholesterol ratio in vulnerable carotid plaque identification
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the predictive value of the thyroid-stimulating hormone to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (THR) in identifying specific vulnerable carotid artery plaques.
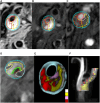
Methods: In this retrospective analysis, we included 76 patients with carotid plaques who met the criteria for admission to Zhejiang Hospital from July 2019 to June 2021. High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging (HRMRI) and the MRI-PlaqueView vascular plaque imaging diagnostic system were utilized to analyze carotid artery images for the identification of specific plaque components, including the lipid core (LC), fibrous cap (FC), and intraplaque hemorrhage (IPH), and recording of the area percentage of LC and IPH, as well as the thickness of FC. Patients were categorized into stable plaque and vulnerable plaque groups based on diagnostic criteria for vulnerable plaques derived from imaging. Plaques were categorized based on meeting one of the following consensus criteria for vulnerability: lipid core area over 40% of total plaque area, fibrous cap thickness less than 65 um, or the presence of intraplaque hemorrhage. Plaques meeting the above criteria were designated as the LC-associated vulnerable plaque group, the IPH-associated group, and the FC-associated group. Multivariate logistic regression was employed to analyze the factors influencing carotid vulnerable plaques and specific vulnerable plaque components. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to assess the predictive value of serological indices for vulnerable carotid plaques.
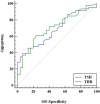
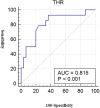
Results: We found that THR (OR = 1.976; 95% CI = 1.094-3.570; p = 0.024) and TSH (OR = 1.939, 95% CI = 1.122-3.350, p = 0.018) contributed to the formation of vulnerable carotid plaques. THR exhibited an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.704 (95% CI = 0.588-0.803) (p = 0.003), and the AUC for TSH was 0.681 (95% CI = 0.564-0.783) (p = 0.008). THR was identified as an independent predictor of LC-associated vulnerable plaques (OR = 2.117, 95% CI = 1.064-4.212, p = 0.033), yielding an AUC of 0.815. THR also demonstrated diagnostic efficacy for LC-associated vulnerable plaques.
Conclusion: This study substantiated that THR and TSH have predictive value for identifying vulnerable carotid plaques, with THR proving to be a more effective diagnostic indicator than TSH. THR also exhibited predictive value and specificity in the context of LC-associated vulnerable plaques. These findings suggest that THR may be a promising clinical indicator, outperforming TSH in detecting specific vulnerable carotid plaques.
Keywords: carotid vulnerable plaque; component characteristics; high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging; thyroid-stimulating hormone; thyroid-stimulating hormone to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio.
© 2024 Lei, Weng, Wang and Qiao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relationship of the Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol/High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio with a Vulnerable Plaque in Patients with Severe Carotid Artery Stenosis: A Case-Control Study in the Han Chinese Population.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2022;19(2):160-170. doi: 10.2174/1567202619666220629160733. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2022. PMID: 35770391
-
MR imaging of vulnerable carotid plaque.Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2020 Aug;10(4):1019-1031. doi: 10.21037/cdt.2020.03.12. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2020. PMID: 32968658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of the diagnostic performance of contrast-enhanced ultrasound and high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of histologically defined vulnerable carotid plaque: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Aug 1;14(8):5814-5830. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-540. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 39143999 Free PMC article.
-
Carotid artery perivascular adipose tissue on magnetic resonance imaging: a potential indicator for carotid vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023 Dec 1;13(12):7695-7705. doi: 10.21037/qims-23-280. Epub 2023 Sep 26. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023. PMID: 38106263 Free PMC article.
-
Contemporary carotid imaging: from degree of stenosis to plaque vulnerability.J Neurosurg. 2016 Jan;124(1):27-42. doi: 10.3171/2015.1.JNS142452. Epub 2015 Jul 31. J Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 26230478 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

