Chinese herbal medicine Shufeng Jiedu capsule for mild to moderate COVID-19: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase II trial
- PMID: 38863976
- PMCID: PMC11165997
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1383831
Chinese herbal medicine Shufeng Jiedu capsule for mild to moderate COVID-19: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase II trial
Abstract
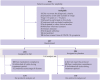
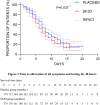
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound global impact, although the majority of recently infected cases have presented with mild to moderate symptoms. Previous clinical studies have demonstrated that Shufeng Jiedu (SFJD) capsule, a Chinese herbal patent medicine, effectively alleviates symptoms associated with the common cold, H1N1 influenza, and COVID-19. This study aimed to assess the efficacy and safety of SFJD capsules in managing symptoms of mild to moderate COVID-19 infection. Methods: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial was conducted from May to December 2022 at two hospitals in China. Mild and moderate COVID-19-infected patients presenting respiratory symptoms within 3 days from onset were randomly assigned to either the SFJD or placebo groups in a 1:1 ratio. Individuals received SFJD capsules or a placebo three times daily for five consecutive days. Participants were followed up for more than 14 days after their RT-PCR nucleoid acid test for SARS-CoV-2 turned negative. The primary outcome measure was time to alleviate COVID-19 symptoms from baseline until the end of follow-up. Results: A total of 478 participants were screened; ultimately, 407 completed the trial after randomization (SFJD, n = 203; placebo, n = 204). No statistically significant difference in baseline parameters was observed between the two groups. The median time to alleviate all symptoms was 7 days in the SFJD group compared to 8 days in the placebo group (p = 0.037). Notably, the SFJD group significantly attenuated fever/chills (p = 0.04) and headache (p = 0.016) compared to the placebo group. Furthermore, the median time taken to reach normal body temperature within 24 h was reduced by 7 hours in the SFJD group compared to the placebo group (p = 0.033). No deaths or instances of serious or critical conditions occurred during this trial period; moreover, no serious adverse events were reported. Conclusion: The trial was conducted in a unique controlled hospital setting, and the 5-day treatment with SFJD capsules resulted in a 1-day reduction in overall symptoms, particularly headache and fever/chills, among COVID-19-infected participants with mild or moderate symptoms. Compared to placebo, SFJD capsules were found to be safe with fewer side effects. SFJD capsules could potentially serve as an effective treatment for alleviating mild to moderate symptoms of COVID-19. Clinical Trial Registration: https://www.isrctn.com/, identifier ISRCTN14236594.
Keywords: COVID-19; Chinese herbal medicine; Shufeng Jiedu capsules; randomized control trial; symptom relief.
Copyright © 2024 Lu, Yang, Jin, Friedemann, Li, Liu, Chen, Zou, Zhang, Wang, Lin, Tang, Cao, Jiang, Gao, Liu, Tao, Robinson, Schröder, Liu and Lu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Shufeng Jiedu capsule for acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a protocol of multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.BMJ Open. 2023 Sep 29;13(9):e070864. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-070864. BMJ Open. 2023. PMID: 37775286 Free PMC article.
-
The add-on effect of Shufeng Jiedu capsule for treating COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Oct 13;9:1020286. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1020286. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36325392 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese Patent Medicine Shufeng Jiedu Capsules as an Adjuvant Therapy for Community-Acquired Pneumonia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 4;13:923395. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.923395. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35860018 Free PMC article.
-
Shufeng Jiedu capsules for treating acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020 May 24;20(1):151. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-02924-5. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020. PMID: 32448238 Free PMC article.
-
Treating acute exacerbations of COPD with Chinese herbal medicine to aid antibiotic use reduction (Excalibur): a randomised double-blind, placebo-controlled feasibility trial.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 25;14:1221905. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1221905. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37818189 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
An advanced network pharmacology investigation of Shufeng Jiedu formula in the treatment for respiratory tract infection based on LC-MS, data mining, molecular docking, and molecular dynamic simulation.Brief Bioinform. 2025 Jul 2;26(4):bbaf353. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaf353. Brief Bioinform. 2025. PMID: 40794954 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine for Viral Pneumonia Therapy: Pharmacological Basis and Mechanistic Insights.Int J Biol Sci. 2025 Jan 6;21(3):989-1013. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.105086. eCollection 2025. Int J Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39897040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shufeng Jiedu Granule against mild COVID-19: Protocol of the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-center heal-COVID phase III study.Chin Herb Med. 2025 Apr 24;17(3):601-608. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2025.04.005. eCollection 2025 Jul. Chin Herb Med. 2025. PMID: 40734912 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bryant A., Lawrie T. A., Dowswell T., Fordham E. J., Mitchell S., Hill S. R., et al. (2021). Ivermectin for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 infection: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis to inform clinical guidelines. Am. J. Ther. 28 (4), e434–e460. 10.1097/MJT.0000000000001402 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clemency B. M., Varughese R., Gonzalez-Rojas Y., Morse C. G., Phipatanakul W., Koster D. J., et al. (2022). Efficacy of inhaled ciclesonide for outpatient treatment of adolescents and adults with symptomatic COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 182 (1), 42–49. 10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.6759 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous