Laryngeal Foreign Body Aspiration in Infancy: A Diagnostic Challenge
- PMID: 38864055
- PMCID: PMC11166228
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.60144
Laryngeal Foreign Body Aspiration in Infancy: A Diagnostic Challenge
Abstract
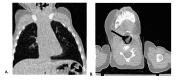
Foreign body aspiration (FBA) is a significant cause of accidental death among children, with laryngeal FBA being relatively rare but potentially fatal due to airway obstruction. This report highlights a case of laryngeal FBA in an 11-month-old child, initially misdiagnosed as viral croup. Otolaryngological evaluation, particularly in the case of laryngeal FBA, may facilitate management. An 11-month-old male was brought to the emergency department, presenting with inspiratory stridor following a choking episode. A chest radiograph and CT scan of the chest were read as normal. He was suspected of having croup and treated with dexamethasone and racemic nebulized epinephrine, which led to temporary clinical improvement. The child returned with persistent stridor to the emergency department eight days after his initial visit, prompting an otolaryngological consultation. Flexible laryngoscopy ultimately identified a star-shaped sequin lodged in the glottis. The foreign body was successfully removed via direct laryngoscopy and bronchoscopy (DLB). Following the removal, the patient demonstrated significant improvement and eventually made a full recovery. This case emphasizes the difficulty in diagnosing laryngeal FBA due to its non-specific symptoms and the limitations of imaging techniques. The importance of a thorough clinical history, physical examination, and proper imaging combined with a high index of suspicion is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. Additionally, the report discusses the potential for severe complications if diagnosis and treatment are delayed, highlighting the need for awareness and prompt intervention in suspected laryngeal FBA cases.
Keywords: direct laryngoscopy and bronchoscopy; flexible laryngoscopy; glottic foreign body; laryngeal foreign body aspiration; pediatric foreign body removal.
Copyright © 2024, Guerra et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Foreign body aspiration score (FOBAS) in children- A retrospective cohort study.Eur J Pediatr. 2023 Sep;182(9):4205-4212. doi: 10.1007/s00431-023-05095-w. Epub 2023 Jul 14. Eur J Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37450025
-
Diagnostic evaluation of foreign body aspiration in children: a prospective study.J Pediatr Surg. 2005 Jul;40(7):1122-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2005.03.049. J Pediatr Surg. 2005. PMID: 16034756
-
Delayed diagnosis and treatment of foreign body aspiration in China: the roles played by physician inexperience and lack of bronchoscopy facilities at local treatment centers.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2013 Dec;77(12):2019-22. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2013.09.026. Epub 2013 Oct 5. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2013. PMID: 24139589
-
Use of virtual bronchoscopy in children with suspected foreign body aspiration.J Bras Pneumol. 2009 Sep;35(9):937-41. doi: 10.1590/s1806-37132009000900016. J Bras Pneumol. 2009. PMID: 19820821 Review. English, Portuguese.
-
Pediatric airway foreign bodies.J La State Med Soc. 1998 Apr;150(4):138-41. J La State Med Soc. 1998. PMID: 9610066 Review.
References
-
- Consumer product ingestion and aspiration in children: A 15-year review. Hanba C, Cox S, Bobian M, Svider PF, Gonik NJ, Shkoukani MA, Sheyn A. Laryngoscope. 2017;127:1202–1207. - PubMed
-
- The anesthetic considerations of tracheobronchial foreign bodies in children: a literature review of 12,979 cases. Fidkowski CW, Zheng H, Firth PG. Anesth Analg. 2010;111:1016–1025. - PubMed
-
- Plastic laryngeal foreign bodies in children: a diagnostic challenge. Bloom DC, Christenson TE, Manning SC, Eksteen EC, Perkins JA, Inglis AF, Stool SE. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2005;69:657–662. - PubMed
-
- Foreign body aspiration in children: experience of 1160 cases. Eren S, Balci AE, Dikici B, Doblan M, Eren MN. Ann Trop Paediatr. 2003;23:31–37. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
