Advancements in Artificial Intelligence for Precision Diagnosis and Treatment of Myocardial Infarction: A Comprehensive Review of Clinical Trials and Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 38864061
- PMCID: PMC11164835
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.60119
Advancements in Artificial Intelligence for Precision Diagnosis and Treatment of Myocardial Infarction: A Comprehensive Review of Clinical Trials and Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
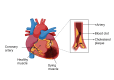
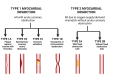
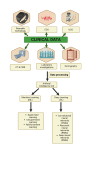
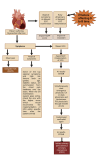
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is still a serious global health issue that has a substantial impact on death and illness rates. The goal of primary prevention strategies is to lower the risk of developing CAD. Nevertheless, current methods usually rely on simple risk assessment instruments that might overlook significant individual risk factors. This limitation highlights the need for innovative methods that can accurately assess cardiovascular risk and offer personalized preventive care. Recent advances in machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) have opened up interesting new avenues for optimizing primary preventive efforts for CAD and improving risk prediction models. By leveraging large-scale databases and advanced computational techniques, AI has the potential to fundamentally alter how cardiovascular risk is evaluated and managed. This review looks at current randomized controlled studies and clinical trials that explore the application of AI and machine learning to improve primary preventive measures for CAD. The emphasis is on their ability to recognize and include a range of risk elements in sophisticated risk assessment models.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; cardiovascular risk factors; coronary artery disease; machine learning; myocardial infarction; primary prevention; risk assessment.
Copyright © 2024, Patel et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
