Application of Urethral Contrast Computed Tomography Three-Dimensional Imaging in the Postoperative Assessment of Prostate Hyperplasia
- PMID: 38864148
- PMCID: PMC11168051
- DOI: 10.1177/15579883241258319
Application of Urethral Contrast Computed Tomography Three-Dimensional Imaging in the Postoperative Assessment of Prostate Hyperplasia
Abstract
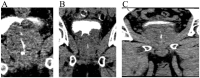
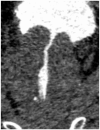
This study assesses the morphological effectiveness of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) surgery using multislice spiral computed tomography three-dimensional imaging (CT3D) with urethral contrast. Twenty-five male patients with BPH and bladder outlet obstruction (BOO) who underwent bipolar transurethral resection of the prostate were selected. Preoperative and postoperative CT3D indicators of retrograde and voiding cystourethrography, including bladder neck diameter, length of the posterior urethra, and degree of prostate protrusion into the bladder and upper and lower diameter of the prostate were used to assess bladder neck and posterior urethra morphology and BOO severity. In addition, preoperative and postoperative International Prostate Symptom Scores and maximum urine flow rates were compared. Postoperative CT3D was used to evaluate changes following obstruction relief postsurgery. Preoperative CT3D indicated significant BOO, whereas postoperative imaging showed improved patency but with irregular posterior urethral lumens and varying degrees of residual glandular tissue. Comparative analysis of preoperative and postoperative bladder outlet metrics revealed significant changes (p < .05). Urethral contrast CT3D effectively visualizes the prostate, bladder neck, and prostatic urethra. It quantifies changes in the urethral lumen postsurgery, correlating the extent of posterior urethral lumen spaciousness with urinary flow rates.
Keywords: bipolar transurethral resection of the prostate; bladder outlet obstruction; prostatic hyperplasia; urethral contrast three-dimensional imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Morphological and clinical evaluation of prostatic urethra using modified sonourethrography with retrograde jelly injection.Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2019 Apr;11(2):O4-O10. doi: 10.1111/luts.12203. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2019. PMID: 29193884
-
Risk factors for urethral stricture and/or bladder neck contracture after monopolar transurethral resection of the prostate for benign prostatic hyperplasia.Urologia. 2018 Nov;85(4):150-157. doi: 10.1177/0391560318758195. Epub 2018 Apr 4. Urologia. 2018. PMID: 30426880
-
Combined prostatic urethral lift and remodeling of the prostate and bladder neck: a modified transurethral approach in the treatment of symptomatic lower urinary tract obstruction.World J Urol. 2018 Jul;36(7):1111-1116. doi: 10.1007/s00345-018-2232-8. Epub 2018 Feb 15. World J Urol. 2018. PMID: 29450732
-
Can prostate stents be used to predict the outcome of transurethral resection of the prostate in the difficult cases?Curr Opin Urol. 2004 Jan;14(1):35-9. doi: 10.1097/00042307-200401000-00008. Curr Opin Urol. 2004. PMID: 15091048 Review.
-
Prostatic urethral lift: a novel approach for managing symptomatic BPH in the aging man.Can J Urol. 2015 Oct;22 Suppl 1:67-74. Can J Urol. 2015. PMID: 26497346 Review.
References
-
- David R. A., Badmus T. A., Salako A. A., Asaleye C. M., Adeloye D., Fanimi O., Opele J. K., Laoye A., Akinbola I. A., Igbokwe M. C., Babalola R. N., Onyeze C. I. (2020). Diagnostic performance of transrectal ultrasound for prostate volume estimation in men with benign prostate hyperplasia. International Journal of Clinical Practice, 74(11), e13615. 10.1111/ijcp.13615 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gabr A. H., Abdelatif A., Sharkawy M. S. E., Hakim A., Batnanonuy A. E., Eissawy M., Ali A. (2022). Benign prostatic hyperplasia morphological parameters for assessing risk of acute urinary retention. African Journal of Urology, 28(25), 1–6. 10.1186/s12301-022-00294-7 - DOI
-
- Garg G., Sankhwar S. N., Goel A., Pandey S., Sharma D., Parihar A. (2019). Evaluation of resistive index of the prostate and bladder sonomorphologic parameters as replacements for urodynamics to predict bladder outlet obstruction in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Luts Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms, 11(3), 163–168. 10.1111/luts.12256 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

