Aesthetic assessment of maxillary lateral and canine implant-supported crowns by laypersons and orthodontists
- PMID: 38864178
- PMCID: PMC11302503
- DOI: 10.2340/aos.v83.40738
Aesthetic assessment of maxillary lateral and canine implant-supported crowns by laypersons and orthodontists
Abstract
Introduction: The objectives of this study were to evaluate how laypersons and orthodontists evaluate and rank aesthetic parameters of an implant-supported crown (ISC) on the canine position (ISC-C) and lateral position (ISC-L).
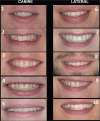
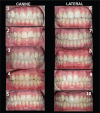
Methods: A digital survey of 11 cases, 5 ISC-C, 5 ISC-L and 1 control case without ISC, was distributed to 207 laypersons and 296 orthodontists. All cases included one extraoral photograph and three intraoral photographs. The respondents were asked to identify the ISC and to evaluate the aesthetic parameters regarding colour of the implant (CI), shape of the implant (SI) and gingival colour around ISC (GCI). Differences within and between the groups were tested using Chi-2-test and Independent-Samples t-test.
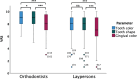
Results: All invited laypersons and 184 orthodontists (62% response rate) answered the survey. Orthodontists (89%) more correctly identified the ISC, regardless of its position, than laypersons (50%) (p < 0.001). Both laypersons (54%) and orthodontists (23%) rated higher proportions of acceptance of CI, SI and GCI in favour for the ISC-L than ISC-C (laypersons: 40%, orthodontists: 10%) (p < 0.001). Assessing each parameter separately, orthodontists rated higher for ISC-L, compared to the ISC-C (p < 0.001). In general, laypersons and orthodontist ranked tooth colour (mean, standard deviation [SD]:8.0,1.5 and 9.0, 1.0) and tooth shape (mean, SD: 8.0, 1.7 and 8.8, 1.2) as aesthetically higher than the gingival colour (mean, SD: 7.2, 2.2 and 8.0, 1.7) (p > 0.001). Conclusion: Laypersons and orthodontists consider the ISC-L as aesthetically more preferable, compared to the ISC-C.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Influence of symmetric and asymmetric alterations of maxillary canine gingival margin on the perception of smile esthetics among orthodontists, dentists, and laypersons.Indian J Dent Res. 2016 Nov-Dec;27(6):586-591. doi: 10.4103/0970-9290.199593. Indian J Dent Res. 2016. PMID: 28169254
-
Implant-supported crowns on maxillary laterals and canines-a long-term follow-up of aesthetics and function.Clin Oral Investig. 2023 Dec;27(12):7545-7555. doi: 10.1007/s00784-023-05344-0. Epub 2023 Nov 9. Clin Oral Investig. 2023. PMID: 37940682 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of maxillary lateral incisor width ratio on perception of smile esthetics among orthodontists and laypersons.J Esthet Restor Dent. 2021 Apr;33(3):510-515. doi: 10.1111/jerd.12664. Epub 2020 Nov 6. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2021. PMID: 33155745
-
Influence of canine vertical position on smile esthetic perceptions by orthodontists and laypersons.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2018 Mar;153(3):371-376. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2017.07.018. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2018. PMID: 29501112
-
Esthetic evaluation of implants vs canine substitution in patients with congenitally missing maxillary lateral incisors: Are there any new insights?Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2016 Sep;150(3):416-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2016.02.025. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2016. PMID: 27585769
References
-
- Cooke J, Wang HL. Canine impactions: incidence and management. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2006;26(5):483–491. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

