Synthesis of novel hybrids of 1,2,3-triazoles-hydrazone: targeting cholinesterases and Alzheimer's related genes
- PMID: 38864182
- PMCID: PMC11370907
- DOI: 10.1080/17568919.2024.2359894
Synthesis of novel hybrids of 1,2,3-triazoles-hydrazone: targeting cholinesterases and Alzheimer's related genes
Abstract
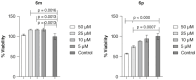
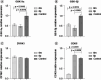
Aim: A new series of 1,2,3-triazole-hydrazone derivatives were developed to evaluate their anti-Alzheimer's activity. Materials & methods: All compounds were screened toward cholinesterases via the modified Ellman's method. The toxicity assay on SH-SY5Y cells was performed using the MTT assay, and the expression levels of GSK-3α, GSK-3β, DYRK1 and CDK5 were assessed in the presence of compounds 6m and 6p.Results:6m and 6p; acting as mixed-type inhibitors, exhibited promising acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitory activity, respectively. 6m demonstrated no toxicity under tested concentrations on the SH-SY5Y cells and positively impacted neurodegenerative pathways. Notably, 6m displayed a significant downregulation in mRNA levels of GSK-3α, GSK-3β and CDK5.Conclusion: The target compounds could be considered in developing anti-Alzheimer's disease agents.
Keywords: 1,2,3-Triazoles; AChE; Alzheimer's; BChE; CDK5; GSK-3α; GSK-3β; Hydrazones.
Plain language summary
[Box: see text].
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests or relevant affiliations with any organization or entity with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants or patents received or pending, or royalties.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
