Triglyceride-glucose index and prognosis in individuals afflicted with heart failure and chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 38864260
- PMCID: PMC11424337
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.14898
Triglyceride-glucose index and prognosis in individuals afflicted with heart failure and chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Background: The triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index has demonstrated correlations with adverse clinical outcomes in patients with ischaemic stroke, coronary heart disease and cardiac failure. However, its association with overall mortality in individuals concurrently experiencing heart failure (HF) and chronic kidney disease (CKD) remains inadequately explored.
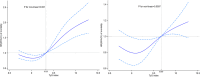
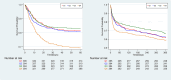
Methods: Utilizing the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care IV (Version 2.2) repository, subjects underwent quartile stratification based on the TyG index. The primary endpoint was all-cause mortality during hospitalization. Cox proportional hazard models were employed to examine the correlation between TyG and all-cause mortality in HF patients with CKD. Evaluation involved Kaplan-Meier (KM) analysis and restricted cubic splines (RCSs) to compare mortality rates during hospitalization and 1 year after admission across cohorts with varying TyG index levels.
Results: A cohort of 1537 HF and CKD patients participated. Cox regression analysis revealed elevated TyG levels as an independent risk factor for both in-hospital and 1 year mortality. RCS analysis indicated a rising, non-linear association between TyG levels and all-cause mortality (P value for non-linear <0.001). KM survival curves demonstrated a statistically significant reduction in survival rates within the high TyG index group compared with the low one (log-rank P < 0.001).
Conclusions: The TyG index exhibited substantial independent prognostic value for elevated in-hospital and 1 year all-cause mortality among the cohort with HF and CKD. These findings suggest that assessing the TyG index could play a crucial role in developing novel therapeutic strategies to improve outcomes for this high-risk demographic.
Keywords: MIMIC‐IV database; chronic kidney disease (CKD); heart failure (HF); hospital and 1 year mortality; prognostic indicator; triglyceride–glucose (TyG) index.
© 2024 The Author(s). ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Triglyceride glucose index is a risk factor for heart failure: A prospective cohort study.ESC Heart Fail. 2024 Dec;11(6):3833-3841. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14963. Epub 2024 Jul 17. ESC Heart Fail. 2024. PMID: 39016168 Free PMC article.
-
Triglyceride glucose index: a significant prognostic marker of heart failure in patients with chronic kidney disease.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(2):2432547. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2432547. Epub 2024 Nov 27. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 39604204 Free PMC article.
-
Association between triglyceride-glucose index and all cause mortality in critically ill patients with heart failure.Sci Rep. 2025 May 9;15(1):16157. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-00129-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40346064 Free PMC article.
-
Association between triglyceride glucose-body mass and one-year all-cause mortality of patients with heart failure: a retrospective study utilizing the MIMIC-IV database.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023 Nov 8;22(1):309. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-02047-4. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023. PMID: 37940979 Free PMC article.
-
Triglyceride-glucose index: a novel evaluation tool for all-cause mortality in critically ill hemorrhagic stroke patients-a retrospective analysis of the MIMIC-IV database.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Mar 18;23(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02193-3. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 38500198 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Triglyceride-glucose index is associated with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in different metabolic states in patients with coronary heart disease.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Nov 4;15:1447072. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1447072. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39558978 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the blood urea nitrogen to serum albumin ratio and the risk of mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease: a cohort study.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Jun 3;26(1):275. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04214-z. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40462012 Free PMC article.
-
Association of the triglyceride-glucose index with cardiovascular mortality risk and competing risks in arthritis patients.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 28;14(1):31387. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82925-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39733154 Free PMC article.
-
Association between triglyceride-glucose index and clinical outcomes among patients with chronic kidney disease: a meta-analysis.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Feb 6;26(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-03984-w. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39915738 Free PMC article.
-
A meta-analysis of the prognostic value of the TyG index in heart failure.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 24;16:1463647. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1463647. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40778275 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

