Astrocytic PAR1 and mGluR2/3 control synaptic glutamate time course at hippocampal CA1 synapses
- PMID: 38864289
- PMCID: PMC11410382
- DOI: 10.1002/glia.24579
Astrocytic PAR1 and mGluR2/3 control synaptic glutamate time course at hippocampal CA1 synapses
Abstract
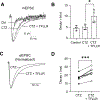
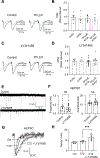
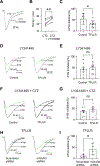
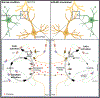
Astrocytes play an essential role in regulating synaptic transmission. This study describes a novel form of modulation of excitatory synaptic transmission in the mouse hippocampus by astrocytic G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). We have previously described astrocytic glutamate release via protease-activated receptor-1 (PAR1) activation, although the regulatory mechanisms for this are complex. Through electrophysiological analysis and modeling, we discovered that PAR1 activation consistently increases the concentration and duration of glutamate in the synaptic cleft. This effect was not due to changes in the presynaptic glutamate release or alteration in glutamate transporter expression. However, blocking group II metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR2/3) abolished PAR1-mediated regulation of synaptic glutamate concentration, suggesting a role for this GPCR in mediating the effects of PAR1 activation on glutamate release. Furthermore, activation of mGluR2/3 causes glutamate release through the TREK-1 channel in hippocampal astrocytes. These data show that astrocytic GPCRs engage in a novel regulatory mechanism to shape the time course of synaptically-released glutamate in excitatory synapses of the hippocampus.
Keywords: PAR1; astrocyte; electrophysiology; glutamate; mGluR2/3.
© 2024 The Author(s). GLIA published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
S.F.T. is a member of the SAB for Eumentis Therapeutics, Sage Therapeutics, and Combined Brain, is a member of the Medical Advisory Board for the GRIN2B Foundation and the CureGRIN Foundation, is an advisor to GRIN Therapeutics and Neurocrine, is co-founder of NeurOp Inc. and Agrithera Inc., and is a member of the Board of Directors of NeurOp Inc.
Figures


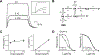


References
-
- Aronica E, Gorter JA, Ijlst-Keizers H, Rozemuller AJ, Yankaya B, Leenstra S, & Troost D. (2003). Expression and functional role of mGluR3 and mGluR5 in human astrocytes and glioma cells: opposite regulation of glutamate transporter proteins. Eur J Neurosci, 17(10), 2106–2118. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2003.02657.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aronica E, van Vliet EA, Mayboroda OA, Troost D, da Silva FH, & Gorter JA. (2000). Upregulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR3 and mGluR5 in reactive astrocytes in a rat model of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Eur J Neurosci, 12(7), 2333–2344. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2000.00131.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

