miR-34a promotes the immunosuppressive function of multiple myeloma-associated macrophages by dampening the TLR-9 signaling
- PMID: 38864479
- PMCID: PMC11167606
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.7387
miR-34a promotes the immunosuppressive function of multiple myeloma-associated macrophages by dampening the TLR-9 signaling
Abstract
Background: Promising outcomes have been observed in multiple myeloma (MM) with the use of immunotherapies, specifically chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cell therapy. However, a portion of MM patients do not respond to CAR-T therapy, and the reasons for this lack of response remain unclear. The objective of this study was to investigate the impact of miR-34a on the immunosuppressive polarization of macrophages obtained from MM patients.
Methods: The levels of miR-34a and TLR9 (Toll-like receptor 9) were examined in macrophages obtained from both healthy individuals and patients with MM. ELISA was employed to investigate the cytokine profiles of the macrophage samples. Co-culture experiments were conducted to evaluate the immunomodulatory impact of MM-associated macrophages on CAR-T cells.
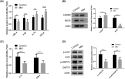
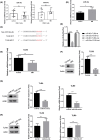
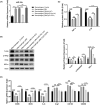
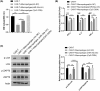
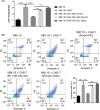
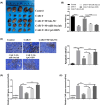
Results: There was an observed suppressed activation of macrophages and CD4+ T lymphocytes in the blood samples of MM patients. Overexpression of miR-34a in MM-associated macrophages dampened the TLR9 expression and impaired the inflammatory polarization. In both the co-culture system and an animal model, MM-associated macrophages suppressed the activity and tumoricidal effect of CAR-T cells in a miR-34a-dependent manner.
Conclusion: The findings imply that targeting the macrophage miR-34a/TLR9 axis could potentially alleviate the immunosuppression associated with CAR-T therapy in MM patients.
Keywords: CAR‐T; TLR9; macrophages; miR‐34a; multiple myeloma.
© 2024 The Author(s). Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Current Anti-Myeloma Chimeric Antigen Receptor-T Cells: Novel Targets and Methods.Balkan Med J. 2025 Jul 1;42(4):301-310. doi: 10.4274/balkanmedj.galenos.2025.2025-4-25. Balkan Med J. 2025. PMID: 40619794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leptin Enhances M1 Macrophage Polarization and Impairs Tendon-Bone Healing in Rotator Cuff Repair: A Rat Model.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 May 1;483(5):939-951. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003428. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 39982019
-
Myeloma cell-intrinsic ANXA1 elevation and T cell dysfunction contribute to BCMA-negative relapse after CAR-T therapy.Mol Ther. 2025 Jul 2;33(7):3375-3391. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2025.03.001. Epub 2025 Mar 8. Mol Ther. 2025. PMID: 40057828
-
TIGIT blockade in the context of BCMA-CART cell therapy does not augment efficacy in a multiple myeloma mouse model.Oncoimmunology. 2025 Dec;14(1):2529632. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2025.2529632. Epub 2025 Jul 12. Oncoimmunology. 2025. PMID: 40652308 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis on the Safety and Efficacy of CAR T Cell Therapy Targeting GPRC5D in Patients with Multiple Myeloma: A New Insight in Cancer Immunotherapy.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2025;25(14):1017-1028. doi: 10.2174/0118715206350342241224073809. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39901537
Cited by
-
Selinexor's Immunomodulatory Impact in Advancing Multiple Myeloma Treatment.Cells. 2025 Mar 13;14(6):430. doi: 10.3390/cells14060430. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40136679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress on N6-methyladenosine and non-coding RNA in multiple myeloma.Discov Oncol. 2025 Apr 25;16(1):615. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02386-6. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40281359 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chng WJ, Dispenzieri A, Chim CS, et al. Avet‐Loiseau H; international myeloma working group. IMWG consensus on risk stratification in multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 2014;28(2):269‐277. - PubMed
-
- Gentile M, Morabito F, Martino M, et al. Chemotherapy‐based regimens in multiple myeloma in 2020. Panminerva Med. 2021;63(1):7‐12. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

