Sustained IL-6 and sTNF-αR1 levels after hip fracture predict 5-year mortality: A prospective cohort study from the Baltimore Hip Studies
- PMID: 38864591
- PMCID: PMC11905919
- DOI: 10.1111/jgs.19018
Sustained IL-6 and sTNF-αR1 levels after hip fracture predict 5-year mortality: A prospective cohort study from the Baltimore Hip Studies
Abstract
Background: Persistent inflammation is associated with adverse health outcomes, but its impact on mortality has not been investigated previously among hip fracture patients. This article aims to investigate the influence of changes in levels of cytokines in the 2 months after a hip fracture repair on 5-year mortality.
Methods: This is a prospective cohort study from the Baltimore Hip Studies (BHS) with 191 community-dwelling older men and women (≥65 years) who had recently undergone surgical repair of an acute hip fracture, with recruitment from May 2006 to June 2011. Plasma interleukin-6 (IL-6), soluble tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor1 (sTNFα-R1), and interleukin-1 receptor agonist (IL-1RA) were obtained within 22 days of admission and at 2 months. All-cause mortality over 5 years was determined. Logistic regression analysis tested the associations between the cytokines' trajectories and mortality over 5 years, adjusted for covariates (age, sex, education, body mass index, lower extremity physical activities of daily living, and Charlson comorbidity index).
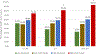
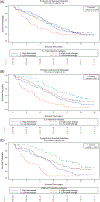
Results: High levels of IL-6 and sTNFα-R1 at baseline with small or no decline at 2 months were associated with higher odds of 5-year mortality compared with those with lower levels at baseline and greater decline at 2 months after adjustment for age, and other potential confounders (OR = 4.71, p = 0.01 for IL-6; OR = 15.03, p = 0.002 for sTNFα-R1). Similar results that failed to reach significance were found for IL-1RA (OR = 2.40, p = 0.18). Those with higher levels of cytokines at baseline with greater decline did not have significantly greater mortality than the reference group, those with lower levels at baseline and greater decline.
Conclusion: Persistent elevation of plasma IL-6 and sTNFα-R1 levels within the first 2 months after hospital admission in patients with hip fracture is associated with higher 5-year mortality. These patients may benefit from enhanced care and earlier intensive interventions to reduce the risk of death.
Keywords: cytokine; fragility fractures; mortality; older adults.
© 2024 The American Geriatrics Society.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
RM is a full-time employee of Novartis Pharmaceuticals, and owns stock in Novartis Pharmaceuticals. MCH has performed consulting activities, including attendance at “virtual” Advisory Board meetings, for the following entities: Acadia Pharmaceuticals, Bioclinica, Eli Lilly, Dompe, Flexion Therapeutics Inc., Genascience, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Kolon TissueGene, Novartis Pharma AG, Pfizer Inc., Regenosine, SFJ Pharmaceuticals Inc., Theralogix LLC, TrialSpark, WCG Analgesics Solutions, and Xalud Therapeutics, and was a member of Data Safety Monitoring Committees for clinical trials coordinated by ACI Clinical, Covance Inc., Cytel, Fortrea, ICON plc, IQVIA, JW Pharma, MiMedRx and PPD. MCH own stock and stock options in Estrato Pharma, Regenosine and Theralogix LLC. JM is on the boards of the Own the Bone Multidisciplinary Advisory Board of the American Orthopedics Association and of the Fragility Fracture Global Network.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Soluble Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Receptor 1, Bone Resorption, and Bone Mineral Density in the Year Following Hip Fractures: The Baltimore Hip Studies.J Bone Miner Res. 2018 Sep;33(9):1649-1656. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3457. Epub 2018 Jun 15. J Bone Miner Res. 2018. PMID: 29734462 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory cytokine levels and depressive symptoms in older women in the year after hip fracture: findings from the Baltimore Hip Studies.J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011 Dec;59(12):2249-55. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03727.x. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011. PMID: 22188073 Free PMC article.
-
Higher serum concentrations of dietary antioxidants are associated with lower levels of inflammatory biomarkers during the year after hip fracture.Clin Nutr. 2012 Oct;31(5):659-65. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2012.01.013. Epub 2012 Feb 25. Clin Nutr. 2012. PMID: 22365613 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive Differences between Men and Women who Fracture their Hip and Impact on Six-Month Survival.J Am Geriatr Soc. 2017 Mar;65(3):e64-e69. doi: 10.1111/jgs.14674. Epub 2017 Feb 8. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2017. PMID: 28176306 Free PMC article.
-
Screening for the primary prevention of fragility fractures among adults aged 40 years and older in primary care: systematic reviews of the effects and acceptability of screening and treatment, and the accuracy of risk prediction tools.Syst Rev. 2023 Mar 21;12(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s13643-023-02181-w. Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36945065 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Anti-inflammatory effect of multi-dose tranexamic acid in hip and knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Mar;33(3):917-928. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01679-0. Epub 2025 Feb 24. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 39992591
References
-
- Paksima N, Koval KJ, Aharanoff G, et al. Predictors of mortality after hip fracture: a 10-year prospective study. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis 2008;66(2):111–117. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

