A Novel Murine Model for Lupus-Like Ocular Chronic Graft-Versus-Host Disease
- PMID: 38864812
- PMCID: PMC11174147
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.65.6.20
A Novel Murine Model for Lupus-Like Ocular Chronic Graft-Versus-Host Disease
Abstract
Purpose: Lupus-like chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD) has been previously described, but the ocular findings have not been elucidated. Recipient mice in a lupus-like cGVHD model manifested notable and persistent ocular surface phenotypes. Herein, we further explored immunopathogenic mechanisms underlying these ocular phenotypes.
Methods: A previously described lupus-like cGVHD model was established by intraperitoneal injection of splenocytes from bm12 mice into C57BL/6J mice. Systemic findings were evaluated for the presence of splenomegaly, proteinuria, and autoantibodies. Comprehensive evaluations were conducted on ocular manifestations and immunopathological features in this model.
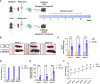
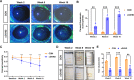
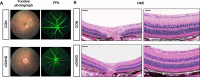
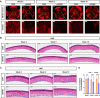
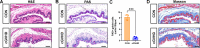
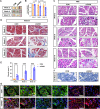
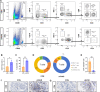
Results: The lupus-like cGVHD model was successfully constructed 2 weeks post-transplantation. The recipient mice developed lupus-like phenotypes, including splenomegaly, proteinuria, and increased autoantibodies, and their ocular presentations included corneal epithelial defects and decreased tear secretion. Histological analysis revealed a reduction in corneal nerve fiber density and corneal endothelial cells, along with conjunctival fibrosis and loss of goblet cells. Moreover, cGVHD induced progressive aggravation of immune cell infiltration and fibrosis in the lacrimal glands. RNA-Sequencing (RNA-seq) results of the lacrimal glands demonstrated that the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between the control and cGVHD groups were associated with GVHD pathways. Immune infiltration analysis using RNA-seq and flow cytometry confirmed that CD8+ T lymphocytes predominantly constituted the inflammatory infiltrating cells within the lacrimal glands.
Conclusions: This lupus-like cGVHD model (bm12→C57BL/6J) exhibited persistent ocular surface manifestations, characterized by immune infiltration of CD8+ T lymphocytes in the lacrimal glands. Thus, this ocular cGVHD model may be used to explore the underlying mechanisms and discover novel therapeutic interventions.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures

References
-
- Westeneng AC, Hettinga Y, Lokhorst H, Verdonck L, van Dorp S, Rothova A.. Ocular graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Cornea. 2010; 29: 758–763. - PubMed
-
- Tabbara KF, Al-Ghamdi A, Al-Mohareb F, et al. .. Ocular findings after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Ophthalmology. 2009; 116: 1624–1629. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

