Tissue-Free Liquid Biopsies Combining Genomic and Methylation Signals for Minimal Residual Disease Detection in Patients with Early Colorectal Cancer from the UK TRACC Part B Study
- PMID: 38864835
- PMCID: PMC11325146
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-24-0226
Tissue-Free Liquid Biopsies Combining Genomic and Methylation Signals for Minimal Residual Disease Detection in Patients with Early Colorectal Cancer from the UK TRACC Part B Study
Abstract
Purpose: The absence of postoperative circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) identifies patients with resected colorectal cancer (CRC) with low recurrence risk for adjuvant chemotherapy (ACT) de-escalation. Our study presents the largest resected CRC cohort to date with tissue-free minimal residual disease (MRD) detection.
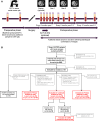
Experimental design: TRACC (tracking mutations in cell-free tumor DNA to predict relapse in early colorectal cancer) included patients with stage I to III resectable CRC. Prospective longitudinal plasma collection for ctDNA occurred pre- and postsurgery, post-ACT, every 3 months for year 1 and every 6 months in years 2 and 3 with imaging annually. The Guardant Reveal assay evaluated genomic and methylation signals. The primary endpoint was 2-year recurrence-free survival (RFS) by postoperative ctDNA detection (NCT04050345).
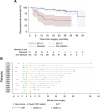
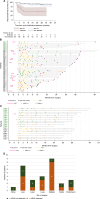
Results: Between December 2016 and August 2022, 1,203 were patients enrolled. Plasma samples (n = 997) from 214 patients were analyzed. One hundred forty-three patients were evaluable for the primary endpoint; 92 (64.3%) colon, 51 (35.7%) rectal; two (1.4%) stage I, 64 (44.8%) stage II, and 77 (53.8%) stage III. Median follow-up was 30.3 months (95% CI, 29.5-31.3). Two-year RFS was 91.1% in patients with ctDNA not detected postoperatively and 50.4% in those with ctDNA detected [HR, 6.5 (2.96-14.5); P < 0.0001]. Landmark negative predictive value (NPV) was 91.2% (95% CI, 83.9-95.9). Longitudinal sensitivity and specificity were 62.1% (95% CI, 42.2-79.3) and 85.9% (95% CI, 78.9-91.3), respectively. The median lead time from ctDNA detection to radiological recurrence was 7.3 months (IQR, 3.3-12.5; n = 9).
Conclusions: Tissue-free MRD detection with longitudinal sampling predicts recurrence in patients with stage I to III CRC without the need for tissue sequencing. The UK TRACC Part C study is currently investigating the potential for ACT de-escalation in patients with undetectable postoperative ctDNA, given the high NPV indicating a low likelihood of residual disease.
©2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
F.M. Marti reports personal fees from Servier and nonfinancial support from Takeda outside the submitted work. L. Bucheit is an employee of Guardant Health. T. Rich is an employee and stockholder of Guardant Health. I. Chau reports personal fees from Eli-Lilly, Bristol Myers Squibb, MSD, Roche, Merck Serono, AstraZeneca, Oncxerna, Boehringer Ingelheim, Incyte, Astella, GSK, Sotio, Eisai, Daiichi-Sankyo, Taiho, Servier, Seagen, Turning Point Therapeutics, Novartis, Takeda, and Elevation Oncology and grants from Janssen-Cilag and Eli Lilly outside the submitted work. D. Cunningham reports grants from Clovis, Eli Lilly, 4SC, Bayer, Celgene, and Roche outside the submitted work and is on the scientific advisory board for OVIBIO. N. Starling reports personal fees from Merck, Novartis, MSD Oncology, Eli Lilly, Pierre Fabre, Amgen, Eli Lilly Bangladesh, GSK, Seagen, BMS, AstraZeneca, and Servier, as well as other support from Merck, AstraZeneca, BMS, Pfizer, Guardant Health, Pfizer, Servier, AstraZeneca, MSD Oncology, Novartis, Guardant Health, Gilead, Seagen, and Janssen outside the submitted work. No disclosures were reported by the other authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Tumor-Naïve ctDNA Assay Detects Minimal Residual Disease in Resected Stage II or III Colorectal Cancer and Predicts Recurrence: Subset Analysis from the GALAXY Study in CIRCULATE-Japan.Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Jan 17;31(2):328-338. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-24-2396. Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 39513962 Free PMC article.
-
Minimal Residual Disease using a Plasma-Only Circulating Tumor DNA Assay to Predict Recurrence of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Following Curative Intent Treatment.Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Jul 15;30(14):2964-2973. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-3660. Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38695832 Free PMC article.
-
Early Detection of Molecular Residual Disease and Risk Stratification for Stage I to III Colorectal Cancer via Circulating Tumor DNA Methylation.JAMA Oncol. 2023 Jun 1;9(6):770-778. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2023.0425. JAMA Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37079312 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Tumor DNA as a Real-Time Biomarker for Minimal Residual Disease and Recurrence Prediction in Stage II Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 11;26(6):2486. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062486. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141130 Free PMC article.
-
Minimal residual disease in colorectal cancer. Tumor-informed versus tumor-agnostic approaches: unraveling the optimal strategy.Ann Oncol. 2025 Mar;36(3):263-276. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2024.12.006. Epub 2024 Dec 13. Ann Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39675560 Review.
Cited by
-
N7-methyladenosine-induced SLC7A7 serves as a prognostic biomarker in pan-cancer and promotes CRC progression in colorectal cancer.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 28;14(1):30755. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80885-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39730571 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of the sensitivity of circulating tumor DNA-based liquid biopsy: current approaches and future perspectives.Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2025 Aug 8;6:1002333. doi: 10.37349/etat.2025.1002333. eCollection 2025. Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2025. PMID: 40787067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating tumor DNA methylation detection as biomarker and its application in tumor liquid biopsy: advances and challenges.MedComm (2020). 2024 Nov 9;5(11):e766. doi: 10.1002/mco2.766. eCollection 2024 Nov. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39525954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Value of ctDNA in surveillance of adjuvant chemosensitivity and regimen adjustment in stage III colon cancer: a protocol for phase II multicentre randomised controlled trial (REVISE trial).BMJ Open. 2025 Jan 2;15(1):e090394. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-090394. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 39753246 Free PMC article.
-
Stool and blood biomarkers for colorectal cancer management: an update on screening and disease monitoring.Mol Cancer. 2024 Nov 19;23(1):259. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02174-w. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39558327 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cancer Research UK . Early diagnosis. [cited 2022 Jul 29]. Available from:https://crukcancerintelligence.shinyapps.io/EarlyDiagnosis/.
-
- Argilés G, Tabernero J, Labianca R, Hochhauser D, Salazar R, Iveson T, et al. . Localised colon cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 2020;31:1291–305. - PubMed
-
- Corcoran RB, Chabner BA. Application of cell-free DNA analysis to cancer treatment. N Engl J Med 2018;379:1754–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

