Cardioprotection with Intralipid During Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Surgery on Cardiopulmonary Bypass: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 38864969
- PMCID: PMC12602576
- DOI: 10.1007/s10557-024-07594-w
Cardioprotection with Intralipid During Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Surgery on Cardiopulmonary Bypass: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Purpose: Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) on cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is associated with myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI), which may limit the benefit of the surgery. Both experimental and clinical studies suggest that Intralipid, a lipid emulsion commonly used for parenteral nutrition, can limit myocardial IRI. We therefore aimed to investigate whether Intralipid administered at reperfusion can reduce myocardial IRI in patients undergoing CABG on CPB.
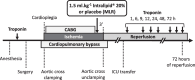
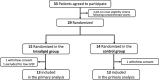
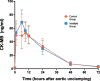
Methods: We conducted a randomized, double-blind, pilot trial in which 29 adult patients scheduled for CABG were randomly assigned (on a 1:1 basis) to receive either 1.5 ml/kg Intralipid 20% or Ringer's Lactate 3 min before aortic cross unclamping. The primary endpoint was the 72-h area under the curve (AUC) for troponin I.
Results: Of the 29 patients randomized, 26 were included in the study (two withdrew consent and one was excluded before surgery). The 72-h AUC for troponin I did not significantly differ between the control and Intralipid group (546437 ± 205518 versus 487561 ± 115724 arbitrary units, respectively; P = 0.804). Other outcomes (including 72-h AUC for CK-MB, C-reactive protein, need for defibrillation, time to extubation, length of ICU and hospital stay, and serious adverse events) were similar between the two groups.
Conclusion: In patients undergoing CABG on CPB, Intralipid did not limit myocardial IRI compared to placebo.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02807727 (registration date: 16 June 2016).
Keywords: Cardioprotection; Coronary artery bypass grafting; Intralipid; Ischemia–reperfusion injury.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics Approval: The trial was authorized by the Human Research Ethics Council (HREC) of the University of Cape Town (number: 806/2014) and by the Medicines Control Council (MCC) of South Africa (number: 20150807). The trial was registered in ClinicalTrials.gov before the start of the study (registration number: NCT02807727) on June 16, 2016. Consent to Participate: The trial was conducted according to the requirements of the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. Consent for Publication: N/A. Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

