Successful Treatment of Severe Pemphigus Vulgaris with Reduced Side Effects Using a Novel IVIg Preparation
- PMID: 38865042
- PMCID: PMC11265024
- DOI: 10.1007/s13555-024-01191-3
Successful Treatment of Severe Pemphigus Vulgaris with Reduced Side Effects Using a Novel IVIg Preparation
Abstract
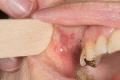
Pemphigus vulgaris (PV) is a rare autoimmune bullous dermatosis (AIBD) characterized by painful blistering of the skin and mucosa caused by autoantibodies that lead to loss of adhesion in the epidermis. Standard therapy for PV is corticosteroids, either alone or in combination with steroid-sparing immunosuppressants or infusions with rituximab. According to the published European guideline, high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) therapy with a dosage of 2 g per kg body weight distributed over 2-5 days every 4 weeks is a promising treatment option, especially for severe or refractory disease. This report describes a 73-year-old female patient with severe and recurrent disease who achieved stabilization with IVIg treatment. However, the patient experienced side effects such as headaches, nausea, and vomiting, which affected daily life. Hence, she was transitioned to a new IVIg preparation with a new manufacturing process, resulting in fewer side effects and an improved quality of life. Further follow-up is necessary to fully evaluate the effectiveness and tolerability of this new IVIg product.
Keywords: Autoimmune disease; High-dose intravenous immunoglobulins; IVIg; Pemphigus vulgaris; Side effects.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Alexander H. Enk received advisory board honoraria, consultancy fees and support for this publication from Biotest AG. Julia K. Winkler received travel expanse and honoraria from Biotest AG. Nadine Wiedenmayer and Anastasia S. Vollmer declare to have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- van Beek N, Zillikens D, Schmidt E. Diagnosis of autoimmune bullous diseases. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2018;16(9):1077–91. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources