User experience of a family health history chatbot: A quantitative analysis
- PMID: 38865081
- PMCID: PMC11391477
- DOI: 10.1177/14604582241262251
User experience of a family health history chatbot: A quantitative analysis
Abstract
Objective: Family health history (FHx) is an important tool in assessing one's risk towards specific health conditions. However, user experience of FHx collection tools is rarely studied. ItRunsInMyFamily.com (ItRuns) was developed to assess FHx and hereditary cancer risk. This study reports a quantitative user experience analysis of ItRuns.
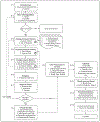
Methods: We conducted a public health campaign in November 2019 to promote FHx collection using ItRuns. We used software telemetry to quantify abandonment and time spent on ItRuns to identify user behaviors and potential areas of improvement.
Results: Of 11,065 users who started the ItRuns assessment, 4305 (38.91%) reached the final step to receive recommendations about hereditary cancer risk. Highest abandonment rates were during Introduction (32.82%), Invite Friends (29.03%), and Family Cancer History (12.03%) subflows. Median time to complete the assessment was 636 s. Users spent the highest median time on Proband Cancer History (124.00 s) and Family Cancer History (119.00 s) subflows. Search list questions took the longest to complete (median 19.50 s), followed by free text email input (15.00 s).
Conclusion: Knowledge of objective user behaviors at a large scale and factors impacting optimal user experience will help enhance the ItRuns workflow and improve future FHx collection.
Keywords: chatbot; family health history; health information technology; telemetry; user behavior; user experience.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: Dr Welch is a shareholder of Doxy.me Inc, Dokbot LLC, ItRunsInMyFamily.com, and Adhere.ly LLC, all of which integrate Dokbot into their software solutions. Heath Morrison is a shareholder of Doxy.me Inc, Dokbot LLC and ItRunsInMyFamily.com. Dr Schiffman is an employee of PEEL Therapeutics, has ownership interests in ItRunsInMyFamily.com and PEEL Therapeutics and serves in a consulting role in N-of-One and Fabric Genomics. Dr Bunnell holds a leadership position in Doxy.me Inc and is a shareholder of Adhere.ly LLC. Authors Hiral Soni, Dinko Vasilev, Triton Ong, Hattie Wilczewski, Alexa Narma, Julia Ivanova are employees of Doxy.me, Inc, a commercial telemedicine company and declare no conflict of interest. Other authors report no other conflicts of interest.
Figures
Update of
-
User experience of a family health history chatbot: A quantitative analysis.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 May 3:rs.3.rs-2886804. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2886804/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Health Informatics J. 2024 Apr-Jun;30(2):14604582241262251. doi: 10.1177/14604582241262251. PMID: 37205400 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
User experience of a family health history chatbot: A quantitative analysis.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 May 3:rs.3.rs-2886804. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2886804/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Health Informatics J. 2024 Apr-Jun;30(2):14604582241262251. doi: 10.1177/14604582241262251. PMID: 37205400 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Usability, Engagement, and Report Usefulness of Chatbot-Based Family Health History Data Collection: Mixed Methods Analysis.J Med Internet Res. 2024 Sep 30;26:e55164. doi: 10.2196/55164. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 39348188 Free PMC article.
-
Using a Chatbot to Assess Hereditary Cancer Risk.JCO Clin Cancer Inform. 2020 Sep;4:787-793. doi: 10.1200/CCI.20.00014. JCO Clin Cancer Inform. 2020. PMID: 32897737 Free PMC article.
-
Review and Comparison of Electronic Patient-Facing Family Health History Tools.J Genet Couns. 2018 Apr;27(2):381-391. doi: 10.1007/s10897-018-0235-7. Epub 2018 Mar 6. J Genet Couns. 2018. PMID: 29512060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transforming Health Care Through Chatbots for Medical History-Taking and Future Directions: Comprehensive Systematic Review.JMIR Med Inform. 2024 Aug 29;12:e56628. doi: 10.2196/56628. JMIR Med Inform. 2024. PMID: 39207827 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Revolutionizing Medicine: Chatbots as Catalysts for Improved Diagnosis, Treatment, and Patient Support.Cureus. 2025 Mar 21;17(3):e80935. doi: 10.7759/cureus.80935. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40255778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contrasting rule and machine learning based digital self triage systems in the USA.NPJ Digit Med. 2024 Dec 27;7(1):381. doi: 10.1038/s41746-024-01367-3. NPJ Digit Med. 2024. PMID: 39725711 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Miroševič Š, Krajc K, Klemenc-Ketiš Z, et al. Mapping users’ experience of a family history and genetic risk algorithm tool in primary care. Public Health Genomics. 2021; 25(1–2): 1–10. - PubMed
-
- Cohn WF, Ropka ME, Pelletier SL, et al. Health Heritage© a web-based tool for the collection and assessment of family health history: initial user experience and analytic validity. Public Health Genomics 2010; 13: 477–491. - PubMed
-
- Jovanovic M, Baez M and Casati F. Chatbots as conversational healthcare services. IEEE Internet Comput 2020; 25: 1–10.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical