Comparative Cardiovascular Risks of Febuxostat and Allopurinol in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 38865287
- PMCID: PMC11484522
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.944314
Comparative Cardiovascular Risks of Febuxostat and Allopurinol in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
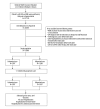
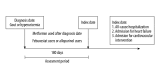
BACKGROUND Hyperuricemia, which is common in chronic kidney disease and diabetes mellitus patients, raises health concerns. Febuxostat, a first-line urate-lowering agent, prompts cardiovascular risk questions, especially in high-risk patients. This study compared the effects of febuxostat and allopurinol on cardiovascular risk in diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease patients. MATERIAL AND METHODS This retrospective observational cohort study, conducted using Taiwan's National Health Insurance Research Database, focused on patients diagnosed with chronic kidney disease and diabetes between January 2012 and December 2017. The study population was divided into 2 groups: allopurinol users (n=12 901) and febuxostat users (n=2997). We performed 1: 1 propensity score matching, resulting in subgroups of 2997 patients each. The primary outcomes were assessed using a competing risk model, estimating hazard ratios (HR) for long-term outcomes, including the risks of all-cause hospitalization, hospitalization for heart failure, and hospitalization for cardiovascular interventions. RESULTS Febuxostat users, compared to allopurinol users, had higher all-cause hospitalization (HR: 1.33; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.25 to 1.42; P<.001), hospitalization for heart failure (HR: 1.62; 95% CI: 1.43 to 1.83; P<.001), and hospitalization for cardiovascular interventions (HR: 1.51; 95% CI: 1.32 to 1.74; P<.001). Moreover, the adverse effects of febuxostat on cardiac health were consistent across most subgroups. CONCLUSIONS Use of febuxostat in patients with diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease is associated with higher cardiovascular risks compared to allopurinol. Prudent evaluation is essential when recommending febuxostat for this at-risk group.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Febuxostat Leads to Better Cardiovascular Outcomes Compared to Allopurinol in Patients With Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease: A Population-Based Cohort Study.Am J Med. 2025 Feb;138(2):236-244.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2024.09.018. Epub 2024 Sep 27. Am J Med. 2025. PMID: 39341524
-
Comparing Cardiovascular Safety of Febuxostat and Allopurinol in the Real World: A Population-Based Cohort Study.Mayo Clin Proc. 2019 Jul;94(7):1147-1157. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2019.03.001. Mayo Clin Proc. 2019. PMID: 31272565
-
Assessment of Cardiovascular Risk in Older Patients With Gout Initiating Febuxostat Versus Allopurinol: Population-Based Cohort Study.Circulation. 2018 Sep 11;138(11):1116-1126. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.033992. Circulation. 2018. PMID: 29899013 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative effect of allopurinol and febuxostat on long-term renal outcomes in patients with hyperuricemia and chronic kidney disease: a systematic review.Clin Rheumatol. 2020 Nov;39(11):3287-3294. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-05079-3. Epub 2020 May 16. Clin Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32418037
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of febuxostat and allopurinol in chronic kidney disease stage 3-5 patients with asymptomatic hyperuricemia: a network meta-analysis.Ren Fail. 2025 Dec;47(1):2470478. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2470478. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Ren Fail. 2025. PMID: 40012480 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The link between hyperuricemia and diabetes: insights from a quantitative analysis of scientific literature.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Feb 7;15:1441503. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1441503. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39991045 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bardin T, Richette P. Definition of hyperuricemia and gouty conditions. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2014;26(2):186–91. - PubMed
-
- Nishizawa H, Maeda N, Shimomura I. Impact of hyperuricemia on chronic kidney disease and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Hypertens Res. 2022;45(4):635–40. - PubMed
-
- Majdan M, Borys O. [Gout and comorbidities associated with hyperuricemia]. Ann Acad Med Stetin. 2010;56(Suppl 1):34–39. [in Polish] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

