Pyramiding of bacterial blight resistance genes into promising restorer BRRI31R line through marker-assisted backcross breeding and evaluation of agro-morphological and physiochemical characteristics of developed resistant restorer lines
- PMID: 38865348
- PMCID: PMC11168670
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0301342
Pyramiding of bacterial blight resistance genes into promising restorer BRRI31R line through marker-assisted backcross breeding and evaluation of agro-morphological and physiochemical characteristics of developed resistant restorer lines
Abstract
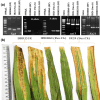
BRRI31R is one of the Bangladesh's most promising restorer lines due to its abundant pollen producing capacity, strong restoring ability, good combining ability, high outcrossing rate and genetically diverse from cytoplasmic male sterile (CMS) line. But the drawback of this line is that it is highly susceptible to bacterial blight (BB) disease of rice caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. The present study highlighted the pyramiding of effective BB resistance genes (xa5, xa13 and Xa21) into the background of BRRI31R, through marker-assisted backcrossing (MABC). Backcross progenies were confirmed and advanced based on the foreground selection of target genes. Pyramided lines were used for pathogenicity test against five Bangladeshi Xanthomonas oryzae (BXo) races (BXo93, BXo220, BXo822, BXo826, BXo887) and confirmed the dominant fertility restore genes, Rf3 and Rf4 and further validated against SNP markers for more confirmation of target resistance genes. All pyramided restorer lines consisted of Xa4 (in built), xa5, xa13, Xa21, and Chalk5 with two fertility restorer genes, Rf3, Rf4. and these restorer lines showed intermediate amylose content (<25%). Restorer lines BRRI31R-MASP3 and BRRI31R-MASP4 showed high levels of resistance against five virulent BXo races and SNP genotyping revealed that these lines also contained a blast resistance gene Pita races. Gene pyramided restorer lines, BRRI31R-MASP3 and BRRI31R-MASP4 can directly be used as a male parent for the development of new BB resistant hybrid rice variety or could be used as a replacement of restorer line of BRRI hybrid dhan5 and 7 to enhance the quality of hybrid seeds as well as rice production in Bangladesh.
Copyright: © 2024 Akter et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Kabir MS, Salam M, Islam A, Sarkar MAR, Mamun M, Rahman M, et al. Doubling rice productivity in Bangladesh: A way to achieving SDG 2 and moving forward. Bangladesh Rice J. 2020;24: 1–47. doi: 10.3329/BRJ.V24I2.53447 - DOI
-
- Kabir M, Salam M, Chowdhury A, Rahman N, Iftekharuddaula K, Rahman M, et al. Rice vision for Bangladesh: 2050 and beyond. Bangladesh Rice J. 2016. doi: 10.3329/brj.v19i2.28160 - DOI
-
- Mezanur-Rahman M, Anamul-Haque M, Arafat-Islam-Nihad S, Mahmudul-Hasan-Akand M, Ruhul-Amin-Howlader M. Morpho-physiological response of Acacia auriculiformis as influenced by seawater induced salinity stress. For Syst. 2016;25: e071. doi: 10.5424/fs/2016253-09386 - DOI
-
- Mamun A Al Rahman MNF, Abdullah Aziz M Qayum MA, Hossain MI Nihad SAI, et al. Identification of meteorological drought prone area in Bangladesh using Standardized Precipitation Index. J Earth Sci Clim Change. 2018;09. doi: 10.4172/2157-7617.1000457 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

