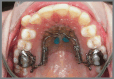
The efficiency of a customized distalizer with Variety SP® screws anchored on palatal miniscrews for upper molar distalization
- PMID: 38865515
- PMCID: PMC11163959
- DOI: 10.1590/2177-6709.29.2.e2423253.oar
The efficiency of a customized distalizer with Variety SP® screws anchored on palatal miniscrews for upper molar distalization
Abstract
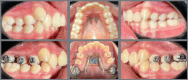
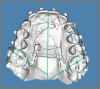
Objective: To assess the effectiveness of a customized distalizer with Variety SP® screws anchored on palatal miniscrews for upper molar distalization.
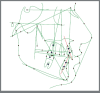
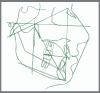
Methods: Seventeen patients aged between 12.5 and 24 years underwent distalization with a customized distalizer. Lateral cephalogram and cast analysis were performed before and after distalization. Linear and angular parameters of the upper first molar, first premolar, and central incisor were assessed.
Results: Distalization with the force passing near the center of resistance (CRes) of the upper first molars resulted in distal movement, with minimal distal tipping (2.8 ± 0.45°, p< 0.05). However, distalization passing occlusal to the CRes led to greater distal tipping (13.6 ± 1.63°, p< 0.05). Statistically significant spontaneous distal tipping and distal movement of the upper first premolars occurred, with a mean of 6.2 ± 1.24° (p< 0.05) and 0.68 ± 0.34 mm (p< 0.05), respectively. The positional change of the upper central incisors presented a mean of -0.23 ± 0.1 mm (p> 0.05) and 2.65 ± 1.1° (p< 0.05). Upper first molar intrusion was statistically significant, with a mean of 0.88 ± 0.2 mm (p< 0.05). Upper right and left first molars rotation towards palatal midline presented mean of 4.1 ± 0.19° (p< 0.05) and 3.4 ± 0.1° (p< 0.05), respectively. Additionally, the distance between upper right and left first molars increased significantly, with a mean of 2.54 ± 0.01 mm (p< 0.05).
Conclusion: The study successfully demonstrated the efficiency of molar distalization without anchorage loss using a customized distalizer anchored on palatal miniscrews.
Objetivo:: Avaliar a eficácia de um distalizador personalizado com parafusos Variety SP® ancorado em mini-implantes palatinos para distalização de molares superiores.
Métodos:: Dezessete pacientes com idade entre 12,5 e 24 anos foram submetidos à distalização com o distalizador customizado. Análises das radiografias cefalométricas laterais e dos modelos de gesso foram realizadas antes e depois da distalização. Foram avaliados parâmetros lineares e angulares dos primeiros molares, primeiros pré-molares e incisivos centrais superiores.
Resultados:: A distalização com a força passando perto do centro de resistência (CRes) dos primeiros molares superiores resultou em distalização com inclinação mínima (2,8 ± 0,45°, p< 0,05). Entretanto, a distalização passando oclusal ao CRes levou a uma maior inclinação para distal (13,6 ± 1,63°, p< 0,05). Ocorreu inclinação distal espontânea e movimento distal estatisticamente significativo dos primeiros pré-molares superiores, com média de 6,2 ± 1,24° (p< 0,05) e 0,68 ± 0,34 mm (p< 0,05), respectivamente. A mudança de posicionamento dos incisivos centrais superiores apresentou média de -0,23 ± 0,1 mm (p> 0,05) e 2,65 ± 1,1° (p< 0,05). A intrusão dos primeiros molares superiores foi estatisticamente significativa, com média de 0,88 ± 0,2 mm (p< 0,05). A rotação dos primeiros molares superiores direito e esquerdo em direção à linha média palatina apresentou média de 4,1 ± 0,19° (p< 0,05) e 3,4 ± 0,1° (p< 0,05), respectivamente. Além disso, a distância entre os primeiros molares superiores direito e esquerdo aumentou significativamente, com média de 2,54 ± 0,01 mm (p< 0,05).
Conclusão:: O estudo demonstrou com sucesso a eficiência da distalização de molares sem perda de ancoragem utilizando um distalizador customizado ancorado em mini-implantes palatinos.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no commercial, proprietary or financial interest in the products or companies described in this article.
Figures
References
-
- Byloff FK, Darendeliler MA. Distal molar movement using the pendulum appliance Part 1: Clinical and radiological evaluation. Angle Orthod. 1997;67(4):249–260. - PubMed
-
- Bussick TJ, McNamara JA., Jr Dentoalveolar and skeletal changes associated with the pendulum appliance. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthod. 2000;117(3):333–343. - PubMed
-
- Kinzinger GS, Gülden N, Yildizhan F, Diedrich PR. Efficiency of a skeletonized distal jet appliance supported by miniscrew anchorage for noncompliance maxillary molar distalization. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthod. 2009;136(4):578–586. - PubMed
-
- Grec RH, Janson G, Branco NC, Moura-Grec PG, Patel MP, Castanha Henriques JF. Intraoral distalizer effects with conventional and skeletal anchorage a meta-analysis. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2013;143(5):602–615. - PubMed
-
- Acar AG, Gürsoy S, Dinçer M. Molar distalization with a pendulum appliance K-loop combination. Eur J Orthod. 2010;32(4):459–465. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

