Biomarkers and prediction of anthracyclic cardiotoxicity in breast cancer
- PMID: 38865526
- PMCID: PMC11164263
- DOI: 10.1590/1806-9282.2024S106
Biomarkers and prediction of anthracyclic cardiotoxicity in breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Chemotherapy with doxorubicin may lead to left ventricular dysfunction. There is a controversial recommendation that biomarkers can predict ventricular dysfunction, which is one of the most feared manifestations of anthracycline cardiotoxicity.
Objective: The aim of this study was to evaluate the behavior of biomarkers such as Troponin I, type B natriuretic peptide, creatine phosphokinase fraction MB, and myoglobin in predicting cardiotoxicity in a cohort of women with breast cancer undergoing chemotherapy with anthracycline.
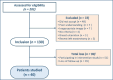
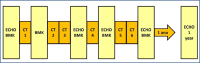
Methods: This is an observational, prospective, longitudinal, unicentric study, which included 40 women with breast cancer, whose therapeutic proposal included treatment with doxorubicin. The protocol had a clinical follow-up of 12 months. Biomarkers such as Troponin I, type B natriuretic peptide, creatine phosphokinase fraction MB, and myoglobin were measured pre-chemotherapy and after the first, third, fourth, and sixth cycles of chemotherapy.
Results: There was a progressive increase in type B natriuretic peptide and myoglobin values in all chemotherapy cycles. Although creatine phosphokinase fraction MB showed a sustained increase, this increase was not statistically significant. Troponin, type B natriuretic peptide, myoglobin, and creatine phosphokinase fraction MB were the cardiotoxicity markers with the earliest changes, with a significant increase after the first chemotherapy session. However, they were not able to predict cardiotoxicity.
Conclusion: Troponin I, type B natriuretic peptide, myoglobin, and creatine phosphokinase fraction MB are elevated during chemotherapy with doxorubicin, but they were not able to predict cardiotoxicity according to established clinical and echocardiographic criteria. The incidence of subclinical cardiotoxicity resulting from the administration of doxorubicin was 12.5%.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: the authors declare there is no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lyon AR, López-Fernández T, Couch LS, Asteggiano R, Aznar MC, Bergler-Klein J, et al. 2022 ESC guidelines on cardio-oncology developed in collaboration with the European hematology association (EHA), the European society for therapeutic radiology and oncology (ESTRO) and the international cardio-oncology society (IC-OS) Eur Heart J. 2022;43(41):4229–4361. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac244. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cardinale D, Sandri MT, Colombo A, Colombo N, Boeri M, Lamantia G, et al. Prognostic value of troponin I in cardiac risk stratification of cancer patients undergoing high-dose chemotherapy. Circulation. 2004;109(22):2749–2754. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000130926.51766.CC. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous