CG001, a C3b-targeted complement inhibitor, blocks 3 complement pathways: development and preclinical evaluation
- PMID: 38865712
- PMCID: PMC11334799
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2024012874
CG001, a C3b-targeted complement inhibitor, blocks 3 complement pathways: development and preclinical evaluation
Abstract
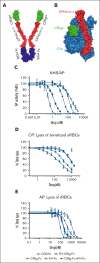
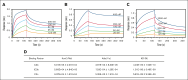
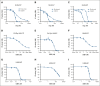
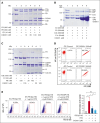
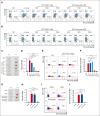
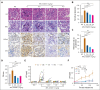
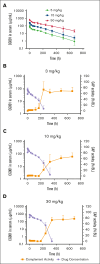
Excessively activated or dysregulated complement activation may contribute to the pathogenesis of a wide range of human diseases, thus leading to a surge in complement inhibitors. Herein, we developed a human-derived and antibody-like C3b-targeted fusion protein (CRIg-FH-Fc) x2, termed CG001, that could potently block all 3 complement pathways. Complement receptor of the immunoglobulin superfamily (CRIg) and factor H (FH) bind to distinct sites in C3b and synergistically inhibit complement activation. CRIg occupancy in C3b prevents the recruitment of C3 and C5 substrates, whereas FH occupancy in C3b accelerates the decay of C3/C5 convertases and promotes the factor I-mediated degradation and inactivation of C3b. CG001 also showed therapeutic effects in alternative pathways-induced hemolytic mouse and classical pathways-induced mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis rat models. In the pharmacological/toxicological evaluation in rats and cynomolgus monkeys, CG001 displayed an antibody-like pharmacokinetic profile, a convincing complement inhibitory effect, and no observable toxic effects. Therefore, CG001 holds substantial potential for human clinical studies.
© 2024 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: W.H. is the inventor of CRIg-FH and CG001, and the founder of ComGen Pharmaceutical. X.L., Luying Lo, and J.Y. are employees of ComGen Pharmaceutical. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel CRIg-targeted complement inhibitor protects cells from complement damage.FASEB J. 2014 Nov;28(11):4986-99. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-258046. Epub 2014 Aug 11. FASEB J. 2014. PMID: 25114177
-
The MFHR1 Fusion Protein Is a Novel Synthetic Multitarget Complement Inhibitor with Therapeutic Potential.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018 Apr;29(4):1141-1153. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2017070738. Epub 2018 Jan 15. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29335241 Free PMC article.
-
A Targeted Complement Inhibitor CRIg/FH Protects Against Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis in Rats via Immune Modulation.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 26;13:746068. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.746068. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35154091 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly and regulation of the complement amplification loop in blood: the role of C3b-C3b-IgG complexes.Mol Immunol. 1999 Sep-Oct;36(13-14):837-42. doi: 10.1016/s0161-5890(99)00104-2. Mol Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10698337 Review.
-
Recombinant generation of two fragments of the rat complement inhibitory factor H [FH(SCR1-7) and FH(SCR1-4)] and their structural and functional characterization in comparison to FH isolated from rat serum.Histol Histopathol. 2006 Jan;21(1):93-102. doi: 10.14670/HH-21.93. Histol Histopathol. 2006. PMID: 16267790 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of complement in tumor immune tolerance and drug resistance: a double-edged sword.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 31;16:1529184. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1529184. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39958348 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yamashina M, Ueda E, Kinoshita T, et al. Inherited complete deficiency of 20-kilodalton homologous restriction factor (CD59) as a cause of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. N Engl J Med. 1990;323(17):1184–1189. - PubMed
-
- Risitano AM, Marotta S. Therapeutic complement inhibition in complement-mediated hemolytic anemias: past, present and future. Semin Immunol. 2016;28(3):223–240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

