REST-dependent downregulation of von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor promotes autophagy in SHH-medulloblastoma
- PMID: 38866867
- PMCID: PMC11169471
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-63371-7
REST-dependent downregulation of von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor promotes autophagy in SHH-medulloblastoma
Abstract
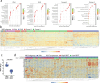
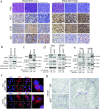
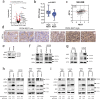
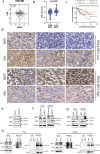
The RE1 silencing transcription factor (REST) is a driver of sonic hedgehog (SHH) medulloblastoma genesis. Our previous studies showed that REST enhances cell proliferation, metastasis and vascular growth and blocks neuronal differentiation to drive progression of SHH medulloblastoma tumors. Here, we demonstrate that REST promotes autophagy, a pathway that is found to be significantly enriched in human medulloblastoma tumors relative to normal cerebella. In SHH medulloblastoma tumor xenografts, REST elevation is strongly correlated with increased expression of the hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF1α)-a positive regulator of autophagy, and with reduced expression of the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) tumor suppressor protein - a component of an E3 ligase complex that ubiquitinates HIF1α. Human SHH-medulloblastoma tumors with higher REST expression exhibit nuclear localization of HIF1α, in contrast to its cytoplasmic localization in low-REST tumors. In vitro, REST knockdown promotes an increase in VHL levels and a decrease in cytoplasmic HIF1α protein levels, and autophagy flux. In contrast, REST elevation causes a decline in VHL levels, as well as its interaction with HIF1α, resulting in a reduction in HIF1α ubiquitination and an increase in autophagy flux. These data suggest that REST elevation promotes autophagy in SHH medulloblastoma cells by modulating HIF1α ubiquitination and stability in a VHL-dependent manner. Thus, our study is one of the first to connect VHL to REST-dependent control of autophagy in a subset of medulloblastomas.
Keywords: Autophagy; Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF1α); Medulloblastoma; REST; Ubiquitination; Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcriptional repressor REST drives lineage stage-specific chromatin compaction at Ptch1 and increases AKT activation in a mouse model of medulloblastoma.Sci Signal. 2019 Jan 22;12(565):eaan8680. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aan8680. Sci Signal. 2019. PMID: 30670636 Free PMC article.
-
Mutant versions of von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) can protect HIF1α from SART1-mediated degradation in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma.Oncogene. 2016 Feb 4;35(5):587-94. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.113. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 25915846
-
MicroRNA-101 targets von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor (VHL) to induce HIF1α mediated apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in normoxia condition.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 4;6:20489. doi: 10.1038/srep20489. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26841847 Free PMC article.
-
Complex cellular functions of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene: insights from model organisms.Oncogene. 2012 May 3;31(18):2247-57. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.442. Epub 2011 Sep 26. Oncogene. 2012. PMID: 21996733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) Tumor Suppressor Gene Function: VHL-HIF Pathway and Advances in Treatments for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC).Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 10;22(18):9795. doi: 10.3390/ijms22189795. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34575959 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Autophagy in brain tumors: molecular mechanisms, challenges, and therapeutic opportunities.J Transl Med. 2025 Jan 13;23(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-06063-0. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39806481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Medulloblastoma: biology and immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 3;16:1602930. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1602930. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40677711 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

