Anti-depressant effect of Naringenin-loaded hybridized nanoparticles in diabetic rats via PPARγ/NLRP3 pathway
- PMID: 38866877
- PMCID: PMC11169681
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-62676-x
Anti-depressant effect of Naringenin-loaded hybridized nanoparticles in diabetic rats via PPARγ/NLRP3 pathway
Abstract
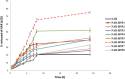
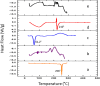
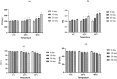
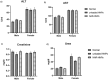
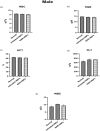
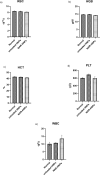
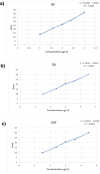
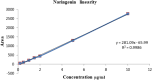
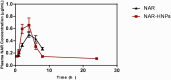
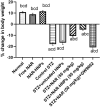
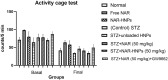
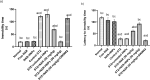
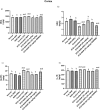
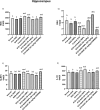
Naringenin (NAR) has various biological activities but low bioavailability. The current study examines the effect of Naringenin-loaded hybridized nanoparticles (NAR-HNPs) and NAR on depression induced by streptozotocin (STZ) in rats. NAR-HNPs formula with the highest in vitro NAR released profile, lowest polydispersity index value (0.21 ± 0.02), highest entrapment efficiency (98.7 ± 2.01%), as well as an acceptable particle size and zeta potential of 415.2 ± 9.54 nm and 52.8 ± 1.04 mV, respectively, was considered the optimum formulation. It was characterized by differential scanning calorimetry, examined using a transmission electron microscope, and a stability study was conducted at different temperatures to monitor its stability efficiency showing that NAR-HNP formulation maintains stability at 4 °C. The selected formulation was subjected to an acute toxicological test, a pharmacokinetic analysis, and a Diabetes mellitus (DM) experimental model. STZ (50 mg/kg) given as a single i.p. rendered rats diabetic. Diabetic rat groups were allocated into 4 groups: one group received no treatment, while the remaining three received oral doses of unloaded HNPs, NAR (50 mg/kg), NAR-HNPs (50 mg/kg) and NAR (50 mg/kg) + peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPAR-γ) antagonist, GW9662 (1mg/kg, i.p.) for three weeks. Additional four non-diabetic rat groups received: distilled water (normal), free NAR, and NAR-HNPs, respectively for three weeks. NAR and NAR-HNPs reduced immobility time in forced swimming test and serum blood glucose while increasing serum insulin level. They also reduced cortical and hippocampal 5-hydroxyindoeacetic acid, 3,4-Dihydroxy-phenylacetic acid, malondialdehyde, NLR family pyrin domain containing-3 (NLRP3) and interleukin-1beta content while raised serotonin, nor-epinephrine, dopamine and glutathione level. PPAR-γ gene expression was elevated too. So, NAR and NAR-HNPs reduced DM-induced depression by influencing brain neurotransmitters and exhibiting anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects through the activation PPAR-γ/ NLRP3 pathway. NAR-HNPs showed the best pharmacokinetic and therapeutic results.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chrysin loaded nanovesicles ameliorated diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Role of NGF/AKT/GSK-3β pathway.Chem Biol Interact. 2023 Apr 25;375:110402. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2023.110402. Epub 2023 Feb 16. Chem Biol Interact. 2023. PMID: 36804429
-
Anti-depressant effect of hesperidin in diabetic rats.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014 Nov;92(11):945-52. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2014-0281. Epub 2014 Sep 19. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25358020
-
Antidepressant and Neuroprotective Effects of Naringenin via Sonic Hedgehog-GLI1 Cell Signaling Pathway in a Rat Model of Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress.Neuromolecular Med. 2019 Sep;21(3):250-261. doi: 10.1007/s12017-019-08538-6. Epub 2019 Apr 29. Neuromolecular Med. 2019. PMID: 31037465
-
Naringin ameliorates cognitive deficits via oxidative stress, proinflammatory factors and the PPARγ signaling pathway in a type 2 diabetic rat model.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Nov;12(5):7093-101. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.4232. Epub 2015 Aug 20. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 26300349
-
Optimization of Naringenin-loaded nanoparticles for targeting of Vanin-1, iNOS, and MCP-1 signaling pathway in HFD-induced obesity.Int J Pharm. 2024 Apr 10;654:123967. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.123967. Epub 2024 Mar 2. Int J Pharm. 2024. PMID: 38438083
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

