Conserved epigenetic hallmarks of T cell aging during immunity and malignancy
- PMID: 38867059
- PMCID: PMC11333289
- DOI: 10.1038/s43587-024-00649-5
Conserved epigenetic hallmarks of T cell aging during immunity and malignancy
Abstract
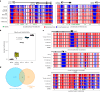
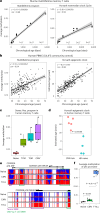
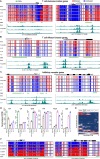
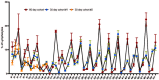
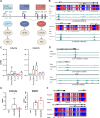
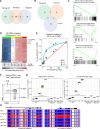
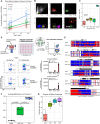
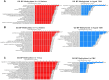
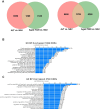
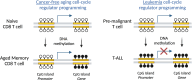
Chronological aging correlates with epigenetic modifications at specific loci, calibrated to species lifespan. Such 'epigenetic clocks' appear conserved among mammals, but whether they are cell autonomous and restricted by maximal organismal lifespan remains unknown. We used a multilifetime murine model of repeat vaccination and memory T cell transplantation to test whether epigenetic aging tracks with cellular replication and if such clocks continue 'counting' beyond species lifespan. Here we found that memory T cell epigenetic clocks tick independently of host age and continue through four lifetimes. Instead of recording chronological time, T cells recorded proliferative experience through modification of cell cycle regulatory genes. Applying this epigenetic profile across a range of human T cell contexts, we found that naive T cells appeared 'young' regardless of organism age, while in pediatric patients, T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia appeared to have epigenetically aged for up to 200 years. Thus, T cell epigenetic clocks measure replicative history and can continue to accumulate well-beyond organismal lifespan.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 AI114442/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI084913/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI084913/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI145024/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- CA238439/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 AI172607/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI144616/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI146032/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 CA238439/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI146032/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K08CA279926/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 AI145024/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA209859/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA279926/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01AI144616/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01AI172607/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01CA237311/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 CA237311/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

