Nomogram for the preoperative prediction of Ki-67 expression and prognosis in stage IA lung adenocarcinoma based on clinical and multi-slice spiral computed tomography features
- PMID: 38867154
- PMCID: PMC11167796
- DOI: 10.1186/s12880-024-01305-5
Nomogram for the preoperative prediction of Ki-67 expression and prognosis in stage IA lung adenocarcinoma based on clinical and multi-slice spiral computed tomography features
Abstract
Objective: This study developed and validated a nomogram utilizing clinical and multi-slice spiral computed tomography (MSCT) features for the preoperative prediction of Ki-67 expression in stage IA lung adenocarcinoma. Additionally, we assessed the predictive accuracy of Ki-67 expression levels, as determined by our model, in estimating the prognosis of stage IA lung adenocarcinoma.
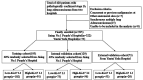
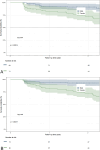
Materials and methods: We retrospectively analyzed data from 395 patients with pathologically confirmed stage IA lung adenocarcinoma. A total of 322 patients were divided into training and internal validation groups at a 6:4 ratio, whereas the remaining 73 patients composed the external validation group. According to the pathological results, the patients were classified into high and low Ki-67 labeling index (LI) groups. Clinical and CT features were subjected to statistical analysis. The training group was used to construct a predictive model through logistic regression and to formulate a nomogram. The nomogram's predictive ability and goodness-of-fit were assessed. Internal and external validations were performed, and clinical utility was evaluated. Finally, the recurrence-free survival (RFS) rates were compared.
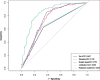
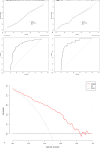
Results: In the training group, sex, age, tumor density type, tumor-lung interface, lobulation, spiculation, pleural indentation, and maximum nodule diameter differed significantly between patients with high and low Ki-67 LI. Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that sex, tumor density, and maximum nodule diameter were significantly associated with high Ki-67 expression in stage IA lung adenocarcinoma. The calibration curves closely resembled the standard curves, indicating the excellent discrimination and accuracy of the model. Decision curve analysis revealed favorable clinical utility. Patients with a nomogram-predicted high Ki-67 LI exhibited worse RFS.
Conclusion: The nomogram utilizing clinical and CT features for the preoperative prediction of Ki-67 expression in stage IA lung adenocarcinoma demonstrated excellent performance, clinical utility, and prognostic significance, suggesting that this nomogram is a noninvasive personalized approach for the preoperative prediction of Ki-67 expression.
Keywords: Ki-67; Lung adenocarcinoma; Nomogram; Tomography; X-ray computed tomography.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Multivariate analysis based on the maximum standard unit value of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography and computed tomography features for preoperative predicting of visceral pleural invasion in patients with subpleural clinical stage IA peripheral lung adenocarcinoma.Diagn Interv Radiol. 2023 Mar 29;29(2):379-389. doi: 10.4274/dir.2023.222006. Epub 2023 Feb 21. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36988049 Free PMC article.
-
A nomogram integrating the clinical and CT imaging characteristics for assessing spread through air spaces in clinical stage IA lung adenocarcinoma.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 11;16:1519766. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1519766. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40292286 Free PMC article.
-
Quantifying invasiveness of clinical stage IA lung adenocarcinoma with computed tomography texture features.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2022 Mar;163(3):805-815.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2020.12.092. Epub 2020 Dec 30. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2022. PMID: 33541730
-
Preoperative Ki-67 proliferation index prediction with a radiomics nomogram in stage T1a-b lung adenocarcinoma.Eur J Radiol. 2022 Oct;155:110437. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2022.110437. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Eur J Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35952476
-
Nomogram using intratumoral and peritumoral radiomics for the preoperative prediction of visceral pleural invasion in clinical stage IA lung adenocarcinoma.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2024 May 31;19(1):307. doi: 10.1186/s13019-024-02807-7. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2024. PMID: 38822379 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Janssen EM, Dy SM, Meara AS, Kneuertz PJ, Presley CJ, Bridges JFP. Survival outcomes in a prospective randomized multicenter phase III trial comparing patients undergoing anatomical segmentectomy versus standard lobectomy for non-small cell lung cancer up to 2 cm. Lung Cancer. 2022;172:108–16. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2022.08.013. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li HH, Qi LN, Ma L, Chen ZS, Xiang BD, Li LQ. Effect of KI-67 positive cellular index on prognosis after hepatectomy in Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage A and B hepatocellular carcinoma with microvascular invasion. Onco Targets Ther. 2018;11:4747–54. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S165244. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

