Identifying therapeutic target genes for migraine by systematic druggable genome-wide Mendelian randomization
- PMID: 38867170
- PMCID: PMC11167905
- DOI: 10.1186/s10194-024-01805-3
Identifying therapeutic target genes for migraine by systematic druggable genome-wide Mendelian randomization
Abstract
Background: Currently, the treatment and prevention of migraine remain highly challenging. Mendelian randomization (MR) has been widely used to explore novel therapeutic targets. Therefore, we performed a systematic druggable genome-wide MR to explore the potential therapeutic targets for migraine.
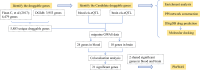
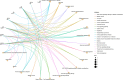
Methods: We obtained data on druggable genes and screened for genes within brain expression quantitative trait locis (eQTLs) and blood eQTLs, which were then subjected to two-sample MR analysis and colocalization analysis with migraine genome-wide association studies data to identify genes highly associated with migraine. In addition, phenome-wide research, enrichment analysis, protein network construction, drug prediction, and molecular docking were performed to provide valuable guidance for the development of more effective and targeted therapeutic drugs.
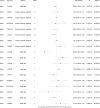
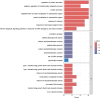
Results: We identified 21 druggable genes significantly associated with migraine (BRPF3, CBFB, CDK4, CHD4, DDIT4, EP300, EPHA5, FGFRL1, FXN, HMGCR, HVCN1, KCNK5, MRGPRE, NLGN2, NR1D1, PLXNB1, TGFB1, TGFB3, THRA, TLN1 and TP53), two of which were significant in both blood and brain (HMGCR and TGFB3). The results of phenome-wide research showed that HMGCR was highly correlated with low-density lipoprotein, and TGFB3 was primarily associated with insulin-like growth factor 1 levels.
Conclusions: This study utilized MR and colocalization analysis to identify 21 potential drug targets for migraine, two of which were significant in both blood and brain. These findings provide promising leads for more effective migraine treatments, potentially reducing drug development costs.
Keywords: Druggable target genes; Mendelian randomization; Migraine.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Conventional and genetic association between migraine and stroke with druggable genome-wide Mendelian randomization.Hum Genet. 2025 Apr;144(4):391-404. doi: 10.1007/s00439-024-02725-7. Epub 2025 Jan 22. Hum Genet. 2025. PMID: 39841246
-
Identification of therapeutic target genes for age-related hearing loss through systematic genome-wide mendelian randomization of druggable genes.Exp Gerontol. 2025 Feb;200:112676. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2025.112676. Epub 2025 Jan 10. Exp Gerontol. 2025. PMID: 39778696
-
Multi-omics Mendelian randomization integrating GWAS, eQTL and pQTL data revealed GSTM4 as a potential drug target for migraine.J Headache Pain. 2024 Jul 22;25(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s10194-024-01828-w. J Headache Pain. 2024. PMID: 39039470 Free PMC article.
-
Migraine genetics: Status and road forward.Cephalalgia. 2023 Feb;43(2):3331024221145962. doi: 10.1177/03331024221145962. Cephalalgia. 2023. PMID: 36759319 Review.
-
Genetic-Driven Druggable Target Identification and Validation.Trends Genet. 2018 Jul;34(7):558-570. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2018.04.004. Epub 2018 May 23. Trends Genet. 2018. PMID: 29803319 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of digital device use on the risk of migraine: a univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study.Front Neurol. 2024 Oct 30;15:1462414. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1462414. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39539656 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic druggable genome-wide Mendelian randomization identifies therapeutic targets for osteoporosis.Osteoporos Sarcopenia. 2025 Jun;11(2):57-64. doi: 10.1016/j.afos.2025.06.001. Epub 2025 Jun 7. Osteoporos Sarcopenia. 2025. PMID: 40677778 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying therapeutic target genes for diabetic retinopathy using systematic druggable genome-wide Mendelian randomization.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2025 Apr 29;17(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s13098-025-01710-y. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2025. PMID: 40301928 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Dysfunction and Dietary Interventions in Migraine Management: The Role of Insulin Resistance and Neuroinflammation-A Narrative and Scoping Review.Brain Sci. 2025 Apr 29;15(5):474. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15050474. Brain Sci. 2025. PMID: 40426647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Andrographolide Mitigates Inflammation and Reverses UVB-Induced Metabolic Reprogramming in HaCaT Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 6;26(13):6508. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136508. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650284 Free PMC article.
References
-
- (2018) Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 38(1):1–211. 10.1177/0333102417738202 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

