Minimally invasive surgeries for spontaneous hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage (MISICH): a multicenter randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 38867192
- PMCID: PMC11170771
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-024-03468-y
Minimally invasive surgeries for spontaneous hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage (MISICH): a multicenter randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) is a common stroke type with high morbidity and mortality. There are mainly three surgical methods for treating ICH. Unfortunately, thus far, no specific surgical method has been proven to be the most effective. We carried out this study to investigate whether minimally invasive surgeries with endoscopic surgery or stereotactic aspiration (frameless navigated aspiration) will improve functional outcomes in patients with supratentorial ICH compared with small-bone flap craniotomy.
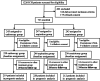
Methods: In this parallel-group multicenter randomized controlled trial conducted at 16 centers, patients with supratentorial hypertensive ICH were randomized to receive endoscopic surgery, stereotactic aspiration, or craniotomy at a 1:1:1 ratio from July 2016 to June 2022. The follow-up duration was 6 months. Patients were randomized to receive endoscopic evacuation, stereotactic aspiration, or small-bone flap craniotomy. The primary outcome was favorable functional outcome, defined as the proportion of patients who achieved a modified Rankin scale (mRS) score of 0-2 at the 6-month follow-up.
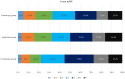
Results: A total of 733 patients were randomly allocated to three groups: 243 to the endoscopy group, 247 to the aspiration group, and 243 to the craniotomy group. Finally, 721 patients (239 in the endoscopy group, 246 in the aspiration group, and 236 in the craniotomy group) received treatment and were included in the intention-to-treat analysis. Primary efficacy analysis revealed that 73 of 219 (33.3%) in the endoscopy group, 72 of 220 (32.7%) in the aspiration group, and 47 of 212 (22.2%) in the craniotomy group achieved favorable functional outcome at the 6-month follow-up (P = .017). We got similar results in subgroup analysis of deep hemorrhages, while in lobar hemorrhages the prognostic outcome was similar among three groups. Old age, deep hematoma location, large hematoma volume, low preoperative GCS score, craniotomy, and intracranial infection were associated with greater odds of unfavorable outcomes. The mean hospitalization expenses were ¥92,420 in the endoscopy group, ¥77,351 in the aspiration group, and ¥100,947 in the craniotomy group (P = .000).
Conclusions: Compared with small bone flap craniotomy, endoscopic surgery and stereotactic aspiration improved the long-term outcome of hypertensive ICH, especially deep hemorrhages.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02811614.
Keywords: Endoscopic surgery; Intracerebral hemorrhage; Minimally invasive surgery; Randomized controlled trial; Small-bone flap craniotomy; Stereotactic aspiration.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical