TEX19 increases the levels of CDK4 and promotes breast cancer by disrupting SKP2-mediated CDK4 ubiquitination
- PMID: 38867223
- PMCID: PMC11170899
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-024-03384-4
TEX19 increases the levels of CDK4 and promotes breast cancer by disrupting SKP2-mediated CDK4 ubiquitination
Abstract
Background: Globally, breast cancer in women is the fifth leading cause of cancer death. There is an urgent need to explore the molecular mechanism of breast cancer proliferation and metastasis.
Method: TCGA database analysis was used to analyze genes expression in breast cancer and normal samples and the association between gene expression and prognosis. Immunohistochemical staining, qPCR and western blotting was sued to detected gene expression. The cell function tests were conducted to investigate the effects of TEX19 and CDK4 with abnormal expression on cell proliferation, migration, apoptosis, cell cycle, and colony formation. Bioinformatics analysis methods combined with CHX tracking experiment and Co-IP experiment were performed to screen and verify the downstream molecule and regulatory mechanism of TEX19. Besides, subcutaneous tumorigenesis model in nude mice was constructed.
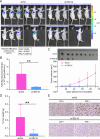
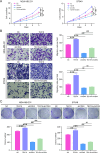
Results: TEX19 was significantly upregulated in breast cancer, and the TEX19 level was related to tumor invasion and prognosis. TEX19 knockdown inhibited the proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells, increased cell apoptosis, and blocked the cell cycle in the G2 phase. Besides, TEX19 suppressed the growth of tumors in the body. Mechanically, TEX19 upregulated the level of CDK4 protein, which depended on the E3 ubiquitin ligase SKP2. Specifically, TEX19 knockdown and SKP2 protein overexpression destroyed the stability of CDK4 protein and enhanced the ubiquitination of CDK4 protein. Additionally, CDK4 knockdown inhibited the proliferation, migration, and colony formation of breast cancer cells, and alleviated the promotion of TEX19 overexpression on the proliferation and migration of breast cancer cell.
Conclusion: TEX19 and CDK4 were upregulated in breast cancer, and TEX19 increased the level of CDK4 protein by influencing SKP2-mediated ubiquitination of CDK4, thereby promoting the progression of breast cancer.
Keywords: Breast cancer; CDK4; TEX19; Ubiquitination.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The steady-state level of CDK4 protein is regulated by antagonistic actions between PAQR4 and SKP2 and involved in tumorigenesis.J Mol Cell Biol. 2017 Oct 1;9(5):409-421. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjx028. J Mol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28992327
-
TEX19 promotes ovarian carcinoma progression and is a potential target for epitope vaccine immunotherapy.Life Sci. 2020 Jan 15;241:117171. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117171. Epub 2019 Dec 13. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31843525
-
SKP2 promotes breast cancer tumorigenesis and radiation tolerance through PDCD4 ubiquitination.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Feb 13;38(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1069-3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30760284 Free PMC article.
-
Human germ/stem cell-specific gene TEX19 influences cancer cell proliferation and cancer prognosis.Mol Cancer. 2017 Apr 26;16(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0653-4. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28446200 Free PMC article.
-
Skp2 in the ubiquitin-proteasome system: A comprehensive review.Med Res Rev. 2020 Sep;40(5):1920-1949. doi: 10.1002/med.21675. Epub 2020 May 11. Med Res Rev. 2020. PMID: 32391596 Review.
Cited by
-
Ballota hirsuta Benth Arrests the Cell Cycle, Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits the Invasion of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 Cell Lines in 2D and 3D Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 13;26(12):5672. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125672. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565136 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

