Progress of single-cell RNA sequencing combined with spatial transcriptomics in tumour microenvironment and treatment of pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 38867230
- PMCID: PMC11167806
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-024-05307-3
Progress of single-cell RNA sequencing combined with spatial transcriptomics in tumour microenvironment and treatment of pancreatic cancer
Abstract
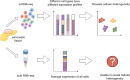
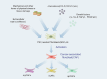
In recent years, single-cell analyses have revealed the heterogeneity of the tumour microenvironment (TME) at the genomic, transcriptomic, and proteomic levels, further improving our understanding of the mechanisms of tumour development. Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) technology allow analysis of the transcriptome at the single-cell level and have unprecedented potential for exploration of the characteristics involved in tumour development and progression. These techniques allow analysis of transcript sequences at higher resolution, thereby increasing our understanding of the diversity of cells found in the tumour microenvironment and how these cells interact in complex tumour tissue. Although scRNA-seq has emerged as an important tool for studying the tumour microenvironment in recent years, it cannot be used to analyse spatial information for cells. In this regard, spatial transcriptomics (ST) approaches allow researchers to understand the functions of individual cells in complex multicellular organisms by understanding their physical location in tissue sections. In particular, in related research on tumour heterogeneity, ST is an excellent complementary approach to scRNA-seq, constituting a new method for further exploration of tumour heterogeneity, and this approach can also provide unprecedented insight into the development of treatments for pancreatic cancer (PC). In this review, based on the methods of scRNA-seq and ST analyses, research progress on the tumour microenvironment and treatment of pancreatic cancer is further explained.
Keywords: Pancreatic cancer; Single-cell RNA sequencing; Spatial transcriptomics; Treatment; Tumour microenvironment.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Single-Cell RNA Sequencing with Spatial Transcriptomics of Cancer Tissues.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 11;23(6):3042. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063042. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel insights from spatial transcriptome analysis in solid tumors.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Sep 4;19(15):4778-4792. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.83098. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37781515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatial transcriptomics in pancreatic cancer: Advances, prospects and challenges.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2024 Nov;203:104430. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2024.104430. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38942220 Review.
-
Deciphering cell-cell interactions and communication in the tumor microenvironment and unraveling intratumoral genetic heterogeneity via single-cell genomic sequencing.Bioengineered. 2022 Jul-Dec;13(7-12):14974-14986. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2023.2185434. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 37105769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-cell RNA sequencing in breast cancer: Understanding tumor heterogeneity and paving roads to individualized therapy.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2020 Aug;40(8):329-344. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12078. Epub 2020 Jul 12. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32654419 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A single-cell perspective on immunotherapy for pancreatic cancer: from microenvironment analysis to therapeutic strategy innovation.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 30;15:1454833. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1454833. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39539544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redefining the tumor microenvironment with emerging therapeutic strategies.Oncol Res. 2024 Oct 16;32(11):1701-1708. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.055161. eCollection 2024. Oncol Res. 2024. PMID: 39449800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer stem cells: landscape, challenges and emerging therapeutic innovations.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Aug 5;10(1):248. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02360-2. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 40759634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-Associated Macrophages: Polarization, Immunoregulation, and Immunotherapy.Cells. 2025 May 19;14(10):741. doi: 10.3390/cells14100741. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40422244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiotherapy and immune microenvironment crosstalk in pancreatic cancer: a comprehensive review of current insights and future directions.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 3;16:1619946. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1619946. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40677710 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen Y-P, Lv J-W, Mao Y-P, Li X-M, Li J-Y, Wang Y-Q, et al. Unraveling Tumour Microenvironment Heterogeneity in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma identifies biologically distinct Immune subtypes Predicting prognosis and immunotherapy responses. Mol Cancer. 2021;20(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01292-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

