KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) therapy based on tepotinib and omeprazole combination
- PMID: 38867255
- PMCID: PMC11167791
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-024-01667-x
KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) therapy based on tepotinib and omeprazole combination
Abstract
Background: KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) shows a relatively low response rate to chemotherapy, immunotherapy and KRAS-G12C selective inhibitors, leading to short median progression-free survival, and overall survival. The MET receptor tyrosine kinase (c-MET), the cognate receptor of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), was reported to be overexpressed in KRAS-mutant lung cancer cells leading to tumor-growth in anchorage-independent conditions.
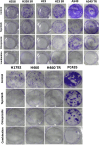
Methods: Cell viability assay and synergy analysis were carried out in native, sotorasib and trametinib-resistant KRAS-mutant NSCLC cell lines. Colony formation assays and Western blot analysis were also performed. RNA isolation from tumors of KRAS-mutant NSCLC patients was performed and KRAS and MET mRNA expression was determined by real-time RT-qPCR. In vivo studies were conducted in NSCLC (NCI-H358) cell-derived tumor xenograft model.
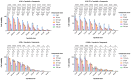
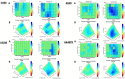
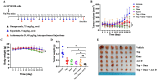
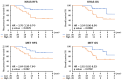
Results: Our research has shown promising activity of omeprazole, a V-ATPase-driven proton pump inhibitor with potential anti-cancer properties, in combination with the MET inhibitor tepotinib in KRAS-mutant G12C and non-G12C NSCLC cell lines, as well as in G12C inhibitor (AMG510, sotorasib) and MEK inhibitor (trametinib)-resistant cell lines. Moreover, in a xenograft mouse model, combination of omeprazole plus tepotinib caused tumor growth regression. We observed that the combination of these two drugs downregulates phosphorylation of the glycolytic enzyme enolase 1 (ENO1) and the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) 5/6 in the H358 KRAS G12C cell line, but not in the H358 sotorasib resistant, indicating that the effect of the combination could be independent of ENO1. In addition, we examined the probability of recurrence-free survival and overall survival in 40 early lung adenocarcinoma patients with KRAS G12C mutation stratified by KRAS and MET mRNA levels. Significant differences were observed in recurrence-free survival according to high levels of KRAS mRNA expression. Hazard ratio (HR) of recurrence-free survival was 7.291 (p = 0.014) for high levels of KRAS mRNA expression and 3.742 (p = 0.052) for high MET mRNA expression.
Conclusions: We posit that the combination of the V-ATPase inhibitor omeprazole plus tepotinib warrants further assessment in KRAS-mutant G12C and non G12C cell lines, including those resistant to the covalent KRAS G12C inhibitors.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
FGTI-2734 Inhibits ERK Reactivation to Overcome Sotorasib Resistance in KRAS G12C Lung Cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2025 Mar;20(3):331-344. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2024.11.022. Epub 2024 Nov 26. J Thorac Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39603412
-
Sotorasib for the treatment of locally advanced/metastatic non-small cell lung cancer.Future Oncol. 2025 Jan;21(1):63-71. doi: 10.1080/14796694.2024.2430172. Epub 2024 Nov 27. Future Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39601038 Review.
-
A cost-effectiveness analysis of sotorasib as second-line treatment for patients with KRAS-G12C-mutated metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (mNSCLC) in Switzerland.Swiss Med Wkly. 2025 Jan 6;155:3777. doi: 10.57187/s.3777. Swiss Med Wkly. 2025. PMID: 39835711
-
Combination therapy of adagrasib and abemaciclib in non-small cell lung cancer brain metastasis models genomically characterized by KRAS-G12C and homozygous loss of CDKN2A.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2025 May 2;13(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s40478-025-01993-2. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2025. PMID: 40317086 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors for metastatic colorectal cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 27;6(6):CD007047. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007047.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28654140 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Omeprazole attenuates irradiation-induced lung injury through the suppression of apoptosis and oxidative stress in mice.Med Oncol. 2025 Apr 22;42(5):172. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02717-1. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40261553
-
KRas plays a negative role in regulating IDO1 expression.Transl Oncol. 2025 Jan;51:102167. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102167. Epub 2024 Nov 16. Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39550890 Free PMC article.
-
Dual inhibition of GTP-bound KRAS and mTOR in lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma harboring KRAS G12C.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 May 11;23(1):220. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02187-y. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40350441 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carrot-Zhang J, Soca-Chafre G, Patterson N, Thorner AR, Nag A, Watson J, et al. Genetic ancestry contributes to somatic mutations in lung cancers from Admixed Latin American populations. Cancer Discov. 2021;11(3):591–8. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-1165. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ruiz-Patiño A, Rodríguez J, Cardona AF, Ávila J, Archila P, Carranza H, et al. p.G12C KRAS mutation prevalence in non-small cell lung cancer: contribution from interregional variability and population substructures among hispanics. Transl Oncol. 2022;15(1):101276. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2021.101276. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Skoulidis F, Goldberg ME, Greenawalt DM, Hellmann MD, Awad MM, Gainor JF, et al. STK11/LKB1 mutations and PD-1 inhibitor resistance in KRAS-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2018;8(7):822–35. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-0099. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

