Associations of RBC counts and incidence of DVT in patients with spinal cord injury: a five year observational retrospective study
- PMID: 38867298
- PMCID: PMC11167836
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-024-04838-1
Associations of RBC counts and incidence of DVT in patients with spinal cord injury: a five year observational retrospective study
Abstract
Background: The role of red blood cell (RBC) counts as potential independent risk factors for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in patients with spinal cord injury (SCI) remains uncertain. This study aims to clarify the associations between RBC counts and DVT incidence among this population.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was performed on 576 patients with SCI admitted to the rehabilitation medicine department from January 1, 2017 to December 31, 2021. After exclusions, 319 patients were analyzed, among which 94 cases of DVT were identified.
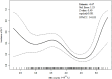
Results: Mode of injury, D-dimer and anticoagulant therapy were significant covariates (P < 0.05). Age, fibrinogen, D-dimer, anticoagulant therapy and American Spinal Cord Injury Association impairment scale (AIS) grades were associated with RBC counts and DVT incidence (P < 0.05). Adjusting for these factors, a 1.00 × 10^12/L increase in RBC counts correlated with a 45% decrease in DVT incidence (P = 0.042), revealing a "U" shaped relationship with a pivot at 4.56 × 10^12/L (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: RBC counts below 4.56 × 10^12/L serve as a protective factor against DVT, while counts above this threshold pose a risk. These findings could inform the development of DVT prevention strategies for patients with SCI, emphasizing the need for targeted monitoring and management of RBC counts.
Keywords: Anticoagulant therapy; D-dimer; Deep vein thrombosis; Fibrinogen; Red blood cell counts; Spinal cord injury.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
D-dimer screening for deep venous thrombosis in traumatic cervical spinal injuries.Spine J. 2015 Nov 1;15(11):2338-44. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2015.06.060. Epub 2015 Jun 28. Spine J. 2015. PMID: 26130085
-
Plasma fibrinogen level is independent risk factor associated with the incidence of pulmonary infection in patients with spinal cord injury: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Pulm Med. 2024 Oct 18;24(1):520. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03332-y. BMC Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 39425165 Free PMC article.
-
Lower red blood cell count is a risk factor for higher D-dimer level in patients with spinal cord injury: A five year retrospective cross-sectional study.J Spinal Cord Med. 2025 Jan 28:1-11. doi: 10.1080/10790268.2025.2452685. Online ahead of print. J Spinal Cord Med. 2025. PMID: 39873595
-
Association of age-adjusted D-dimer with deep vein thrombosis risk in patients with spinal cord injury: a cross-sectional study.Spinal Cord. 2022 Jan;60(1):90-98. doi: 10.1038/s41393-021-00647-z. Epub 2021 Jun 1. Spinal Cord. 2022. PMID: 34075205
-
Duplex ultrasound, clinical score, thrombotic risk, and D-dimer testing for evidence based diagnosis and management of deep vein thrombosis and alternative diagnoses in the primary care setting and outpatient ward.Int Angiol. 2014 Feb;33(1):1-19. Int Angiol. 2014. PMID: 24452081 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

