Development of a postoperative visual function rehabilitation compliance assessment scale for children with congenital cataract: a reliability and validity study
- PMID: 38867303
- PMCID: PMC11167793
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-024-01922-4
Development of a postoperative visual function rehabilitation compliance assessment scale for children with congenital cataract: a reliability and validity study
Abstract
Objective: To develop a comprehensive compliance assessment scale for postoperative visual function rehabilitation in children with congenital cataracts and to assess its reliability and validity.
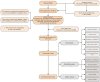
Method: Drawing on the Interactive Model of Health Behavior, we conducted a literature review and semi-structured interviews to create a pool of 36 items. The items underwent rigorous evaluation through the Delphi method, face validity checks, and item analysis, leading to a reduction to 18 items. To assess the scale's reliability and validity, we collected data from 225 parents of children with congenital cataracts. We employed SPSS version 25.0 for data analysis and evaluated construct validity using exploratory factor analysis, content validity, internal consistency reliability, and test-retest reliability.
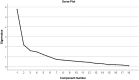
Results: The compliance scale for postoperative visual function rehabilitation in children with congenital cataracts comprises 5 dimensions and 18 items. Exploratory factor analysis extracted 5 common factors, with a cumulative variance contribution rate of 68.178%. Item-level content validity index ranged from 0.730 to 1.000, and the content validity index of the scale was 0.963. The total Cronbach's alpha coefficient, split-half reliability, and test-retest reliability of the scale were 0.855, 0.778, and 0.859, respectively.
Conclusions: The compliance assessment scale for postoperative visual function rehabilitation in children with congenital cataracts demonstrates acceptable reliability and validity. It serves as a valuable reference for developing standardized nursing programs for these children in clinical practice.
Keywords: Compliance; Congenital cataract; Interactive models of health behaviors; Reliability; Scale development; Validity; Visual function rehabilitation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development and validation of the family management scale for children with asthma (FMSCA).J Asthma. 2020 Apr;57(4):441-451. doi: 10.1080/02770903.2019.1571085. Epub 2019 Feb 4. J Asthma. 2020. PMID: 30714838
-
Evaluation of reliability and validity regarding the Chinese version of Critical Cultural Competence Scale for clinical nurses.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Oct 28;47(10):1425-1434. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2022.210695. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 36411694 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. Chinese, English.
-
[Development and validation of the joint function and health assessment scale for juvenile idiopathic arthritis].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Dec 2;62(12):1169-1175. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112140-20240818-00584. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39563045 Chinese.
-
Development and validation of a graduated compression stockings adherence scale.Phlebology. 2023 Oct;38(9):605-612. doi: 10.1177/02683555231200109. Epub 2023 Aug 31. Phlebology. 2023. PMID: 37651292 Review.
-
Development and psychometric evaluation of the Attitudes Towards Recognising Early and Noticeable Deterioration (ATREND) scale.J Clin Nurs. 2023 Jun;32(11-12):2684-2699. doi: 10.1111/jocn.16350. Epub 2022 May 8. J Clin Nurs. 2023. PMID: 35527356 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2023A03J0913/Study on the application of early warning score for children based on artificial intelligence in pediatric emergency department
- 202103000088/Study on the establishment of children myopia prevention and control and eye health network prevention and control system in Shufu County, Kashgar Prefecture, Xinjiang
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical