Iron metabolism and arthritis: Exploring connections and therapeutic avenues
- PMID: 38867424
- PMCID: PMC11268821
- DOI: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003169
Iron metabolism and arthritis: Exploring connections and therapeutic avenues
Abstract
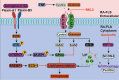
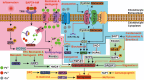
Iron is indispensable for the viablility of nearly all living organisms, and it is imperative for cells, tissues, and organisms to acquire this essential metal sufficiently and maintain its metabolic stability for survival. Disruption of iron homeostasis can lead to the development of various diseases. There is a robust connection between iron metabolism and infection, immunity, inflammation, and aging, suggesting that disorders in iron metabolism may contribute to the pathogenesis of arthritis. Numerous studies have focused on the significant role of iron metabolism in the development of arthritis and its potential for targeted drug therapy. Targeting iron metabolism offers a promising approach for individualized treatment of arthritis. Therefore, this review aimed to investigate the mechanisms by which the body maintains iron metabolism and the impacts of iron and iron metabolism disorders on arthritis. Furthermore, this review aimed to identify potential therapeutic targets and active substances related to iron metabolism, which could provide promising research directions in this field.
Copyright © 2024 The Chinese Medical Association, produced by Wolters Kluwer, Inc. under the CC-BY-NC-ND license.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Dougados M, Baeten D. Spondyloarthritis. Lancet 2011;377:2127–2137. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(11)60071-8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

