Azacitidine as epigenetic priming for chemotherapy is safe and well-tolerated in infants with newly diagnosed KMT2A-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Children's Oncology Group trial AALL15P1
- PMID: 38867582
- PMCID: PMC11609799
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2024.285158
Azacitidine as epigenetic priming for chemotherapy is safe and well-tolerated in infants with newly diagnosed KMT2A-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Children's Oncology Group trial AALL15P1
Abstract
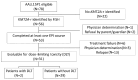
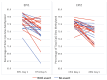
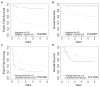
Infants less than 1 year old diagnosed with KMT2A-rearranged (KMT2A-r) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) are at high risk of failure to achieve remission, relapse, and death due to leukemia, despite intensive therapies. Infant KMT2A-r ALL blasts are characterized by DNA hypermethylation. Epigenetic priming with DNA methyltransferase inhibitors increases the cytotoxicity of chemotherapy in preclinical studies. The Children's Oncology Group trial AALL15P1 tested the safety and tolerability of 5 days of azacitidine treatment immediately prior to the start of chemotherapy on day 6, in four post-induction chemotherapy courses for infants with newly diagnosed KMT2A-r ALL. The treatment was well-tolerated, with only two of 31 evaluable patients (6.5%) experiencing dose-limiting toxicity. Whole genome bisulfite sequencing of peripheral blood mononuclear cells demonstrated decreased DNA methylation in 87% of samples tested following 5 days of azacitidine treatment. Event-free survival was similar to that in prior studies of newly diagnosed infant ALL. Azacitidine is safe and results in decreased DNA methylation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in infants with KMT2A-r ALL, but the incorporation of azacitidine to enhance cytotoxicity did not impact survival. Clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT02828358.
Figures

References
-
- Pieters R, De Lorenzo P, Ancliffe P, et al. . Outcome of infants younger than 1 year with acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated with the Interfant-06 protocol: results from an international phase III randomized study. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(25):2246-2256. - PubMed
-
- Pieters R, Schrappe M, De Lorenzo P, et al. . A treatment protocol for infants younger than 1 year with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (Interfant-99): an observational study and a multicentre randomised trial. Lancet. 2007;370(9583):240-250. - PubMed
-
- Tomizawa D, Miyamura T, Imamura T, et al. . A risk-stratified therapy for infants with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a report from the JPLSG MLL-10 trial. Blood. 2020;136(16):1813-1823. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

