The distribution of rennet activity between the cheese aging process and whey is not influenced by the association of enzymes with caseins
- PMID: 38867957
- PMCID: PMC11168479
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32263
The distribution of rennet activity between the cheese aging process and whey is not influenced by the association of enzymes with caseins
Abstract
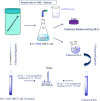
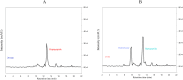
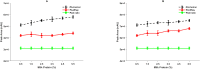
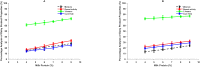
The division of rennet in cheesemaking is split between the curd and whey, influencing the taste and texture of aged cheeses. Our study aimed to examine how raising the protein concentration in reconstituted skim milk (up to 8.8 %) affects the distribution of calf rennet activity (RA) in rennet curds produced through two methods: renting only and renneting with glucono-δ-lactone (GDL) to achieve slow acidification. The distribution of rennet activity (RA) into curds increased as the concentration of skim milk rose, ranging from 8.6 % to 29.1 % without acidification, and from 6.5 % to 19.4 % when combined with slow acidification. This increase seemed to be related to the retention of moisture and protein. Surprisingly, the concentration of residual RA in the whey (measured in international milk clotting units, IMCU/mL) remained unaffected and remained consistent with the initial IMCU/mL of milk. This suggests that the division of RA between curd and whey is not influenced by the association of enzymes with caseins (CNs). Instead, it is possible that the strength of interactions between CNs themselves plays a significant role. These findings could be valuable for research focused on enhancing the cheese aging process.
Keywords: Calf rennet; Milk concentration; Rennet activity partitioning; Rennet curd; Rennet whey.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Production of cheese from donkey milk as influenced by addition of transglutaminase.J Dairy Sci. 2019 Dec;102(12):10867-10876. doi: 10.3168/jds.2019-16615. Epub 2019 Sep 25. J Dairy Sci. 2019. PMID: 31563318
-
Functionality of process cheese made from Cheddar cheese with various rennet levels and high-pressure processing treatments.J Dairy Sci. 2024 Jan;107(1):74-90. doi: 10.3168/jds.2023-23825. Epub 2023 Sep 12. J Dairy Sci. 2024. PMID: 37709025
-
Structural dependence of concentrated skim milk curd on micellar restructuring.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 3;10(1):e24046. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24046. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38230241 Free PMC article.
-
Rennet Coagulation and Cheesemaking Properties of Thermally Processed Milk: Overview and Recent Developments.J Agric Food Chem. 2015 Nov 4;63(43):9389-403. doi: 10.1021/jf504167v. Epub 2015 Mar 10. J Agric Food Chem. 2015. PMID: 25607716 Review.
-
Extent of κ-casein hydrolysis during renneting of bovine milk: A critical assessment of the analytical and estimation approaches.Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Dec 12;12(3):1399-1412. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3868. eCollection 2024 Mar. Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 38455171 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Leveraging Lactobacillus plantarum probiotics to mitigate diarrhea and Salmonella infections in broiler chickens.AMB Express. 2024 Dec 18;14(1):137. doi: 10.1186/s13568-024-01792-3. AMB Express. 2024. PMID: 39694979 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Towns J.K. Moisture content in proteins: its effects and measurement. J. Chromatogr. A. 1995;705(1):115–127. - PubMed
-
- Mirsalami S.M., Alihosseini A. Selection of the most effective kinetic model of lactase hydrolysis by immobilized Aspergillus Niger and free β-galactosidase. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2021;25(12)
-
- Mirsalami S.M., Mirsalami M., Ghodousian A. Techniques for immobilizing enzymes to create durable and effective biocatalysts. Results in Chemistry. 2024
-
- Tidona F., et al. Partial substitution of 40 g/100 g fresh milk with reconstituted low heat skim milk powder in high-moisture mozzarella cheese production: rheological and water-related properties. LWT. 2021;137
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

