Nanoquantification of RUNX2 by a 1,1'-carbonyldiimidazole-diamond mediated sandwich assay for osteogenic differentiation
- PMID: 38868000
- PMCID: PMC11167296
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31837
Nanoquantification of RUNX2 by a 1,1'-carbonyldiimidazole-diamond mediated sandwich assay for osteogenic differentiation
Abstract
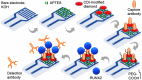
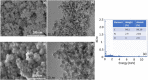
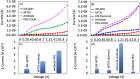
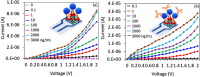
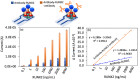
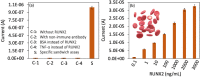
Adipose tissue-derived stem cells (ADSCs) possess the capability to modulate the immune response and alleviate inflammation, rendering them a promising therapeutic option for various conditions, including autoimmune diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and tissue injuries. The osteogenic differentiation in ADSCs plays a pivotal role in fracture healing, bone growth, and the overall bone turnover process, governed by intricate interactions. Runt-related Transcription Factor 2 (RUNX2) is a key player in mineralized tissue generation and is typically found in the early stages of osteogenic differentiation. The objective of this study was to develop a high-affinity sandwich biosensor for the quantification of RUNX2. 1,1'-Carbonyldiimidazole-modified nanodiamond was immobilized on an amine-modified interdigitated electrode surface, followed by the use of a capture antibody to facilitate antigen interaction. A sandwich assay was conducted with the antibody, and the limit of detection for RUNX2 was calculated as 0.1 ng/mL, with a regression value (R2) of 0.9914 over a linear range of 1-2000 ng/mL. Furthermore, biofouling experiments with a nonimmune antibody, BSA, and TNF-α did not yield any current responses, indicating the specific detection of RUNX2. Additionally, RUNX2-spiked serum exhibited an increasing current response at all concentrations, confirming the selective detection of RUNX2.
Keywords: Antibody orientation; Nanodiamond; Runt-related transcription factor; Sandwich pattern.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A promotes the osteogenic differentiation of rat adipose-derived stem cells by altering the epigenetic modifications on Runx2 promoter in a BMP signaling-dependent manner.Stem Cells Dev. 2013 Jan 15;22(2):248-55. doi: 10.1089/scd.2012.0105. Epub 2012 Nov 2. Stem Cells Dev. 2013. PMID: 22873791
-
[Effect of modified titanium loaded with endothelial progenitor cells-exosomes on osteogenic and angiogenic differentiations of adipose-derived stem cells].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022 Aug 15;36(8):1032-1040. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202203132. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35979798 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Runx2 overexpression enhances osteoblastic differentiation and mineralization in adipose--derived stem cells in vitro and in vivo.Calcif Tissue Int. 2006 Sep;79(3):169-78. doi: 10.1007/s00223-006-0083-6. Epub 2006 Sep 11. Calcif Tissue Int. 2006. PMID: 16969589
-
Transcriptional Programming in Arteriosclerotic Disease: A Multifaceted Function of the Runx2 (Runt-Related Transcription Factor 2).Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021 Jan;41(1):20-34. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.313791. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021. PMID: 33115268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcription factor Runx2 and its application to bone tissue engineering.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2012 Sep;8(3):891-7. doi: 10.1007/s12015-011-9337-4. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2012. PMID: 22139789 Review.
References
-
- Carolina, Garcia Latorre Raquel, Martinez-Lorca Alberto, Fernazdez Eva, Hernanz Raul, Martin Mercedes, Dominguez Jose A., Munoz Teresa, Canales Elena, Vallejo Carmen, Alarza Marina, Hervas Asuncion, Garvi Manuel, Pino Vanesa, Sancho Sansoles. Interobserver variability in GTV contouring in non-spine bone metastases. J Clin Transl Res. 2022;8:465–469. doi: 10.18053/jctres.08.202206.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

