Cone-beam CT evaluation of post-extraction alveolar bone changes at the maxillary incisor sites in an East Asian population: A cross-sectional study
- PMID: 38868037
- PMCID: PMC11167353
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32027
Cone-beam CT evaluation of post-extraction alveolar bone changes at the maxillary incisor sites in an East Asian population: A cross-sectional study
Abstract
Objective: Understanding the characteristics of alveolar bone resorption in an East Asian population after maxillary incisor extraction and providing a reference for implant treatment plans.
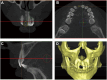
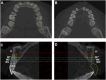
Study design: Cone-beam computerized tomography (CBCT) data of 125 East Asian patients with unilateral extraction of maxillary incisors for 3 months were collected. The alveolar bone width and height in the extraction sites were measured and compared with the corresponding contralateral sites.
Results: The differences in alveolar bone width between the extraction site and contralateral site were as follows: 4.11 mm, 2.68 mm, and 2.09 mm (3 mm, 5 mm, 7 mm apical from CEJ of the contralateral tooth). Data are expressed as the median. The horizontal resorption ratio of alveolar bone was 49.94 %, 31.5 %, and 24.46 %. The difference in alveolar bone height was 0.78 mm. The vertical resorption ratio was 7.78 %. The resorption did not differ significantly between sexes and was not significantly affected by tooth positions.
Conclusions: In the studied East Asian population, significant horizontal and vertical alveolar bone resorption occurs after natural healing of maxillary incisor extraction for 3 months. The closer to the alveolar ridge crest, the more significant the horizontal resorption, resulting in an "inverted triangle" shape residual alveolar bone.
Keywords: Alveolar bone resorption; Cone-beam computerized tomography (CBCT); East Asian; Maxillary incisor; Tooth extraction.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

