Simultaneous measurement of COVID-19 treatment drugs (nirmatrelvir and ritonavir) in rat plasma by UPLC-MS/MS and its application to a pharmacokinetic study
- PMID: 38868075
- PMCID: PMC11168422
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32187
Simultaneous measurement of COVID-19 treatment drugs (nirmatrelvir and ritonavir) in rat plasma by UPLC-MS/MS and its application to a pharmacokinetic study
Abstract
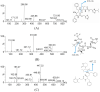
PAXLOVID™ (Co-packaging of Nirmatrelvir with Ritonavir) has been approved for the treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). The goal of the experiment was to create an accurate and straightforward analytical method using ultra performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) to simultaneously quantify nirmatrelvir and ritonavir in rat plasma, and to investigate the pharmacokinetic profiles of these drugs in rats. After protein precipitation using acetonitrile, nirmatrelvir, ritonavir, and the internal standard (IS) lopinavir were separated using ultra performance liquid chromatography (UPLC). This separation was achieved with a mobile phase composed of acetonitrile and an aqueous solution of 0.1% formic acid, using a reversed-phase column with a binary gradient elution. Using multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) technology, the analytes were detected in the positive electrospray ionization mode. Favorable linearity was observed in the calibration range of 2.0-10000 ng/mL for nirmatrelvir and 1.0-5000 ng/mL for ritonavir, respectively, within plasma samples. The lower limits of quantification (LLOQ) attained were 2.0 ng/mL for nirmatrelvir and 1.0 ng/mL for ritonavir, respectively. Both drugs demonstrated inter-day and intra-day precision below 15%, with accuracies ranging from -7.6% to 13.2%. Analytes were extracted with recoveries higher than 90.7% and without significant matrix effects. Likewise, the stability was found to meet the requirements of the analytical method under different conditions. This UPLC-MS/MS method, characterized by enabling accurate and precise quantification of nirmatrelvir and ritonavir in plasma, was effectively utilized for in vivo pharmacokinetic studies in rats.
Keywords: Nirmatrelvir; Pharmacokinetics; Ritonavir; UPLC-MS/MS; rat.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

